Musing on Industrial Time
Posted: April 20, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, time banking, universal principles of design, work/life balance, workload 3 CommentsI caught up with a good friend recently and we were discussing the nature of time. She had stepped back from her job and was now spending a lot of her time with her new-born son. I have gone to working three days a week, hence have also stepped back from the five-day grind. It was interesting to talk about how this change to our routines had changed the way that we thought of and used time. She used a term that I wanted to discuss here, which was industrial time, to describe the clock-watching time of the full-time worker. This is part of the larger area of time discipline, how our society reacts to and uses time, and is really quite interesting. Both of us had stopped worrying about the flow of time in measurable hours on certain days and we just did things until we ran out of day. This is a very different activity from the usual “do X now, do Y in 15 minutes time” that often consumes us. In my case, it took me about three months of considered thought and re-training to break the time discipline habits of thirty years. In her case, she has a small child to help her to refocus her time sense on the now.
Modern time-sense is so pervasive that we often don’t think about some of the underpinnings of our society. It is easy to understand why we have years and, although they don’t line up properly, months given that these can be matched to astronomical phenomena that have an effect on our world (seasons and tides, length of day and moonlight, to list a few). Days are simple because that’s one light/dark cycle. But why there are 52 weeks in a year? Why are there 7 days in a week? Why did the 5-day week emerge as a contiguous block of 5 days? What is so special about working 9am to 5pm?
A lot of modern time descends from the struggle of radicals and unionists to protect workers from the excesses of labour, to stop people being worked to death, and the notion of the 8 hour day is an understandable division of a 24 hour day into three even chunks for work, rest and leisure. (Goodness, I sound like I’m trying to sell you chocolate!)
If we start to look, it turns out that the 7 day week is there because it’s there, based on religion and tradition. Interestingly enough, there have been experiments with other week lengths but it appears hard to shift people who are used to a certain routine and, tellingly, making people wait longer for days off appears to be detrimental to adoption.
If we look at seasons and agriculture, then there is a time to sow, to grow, to harvest and to clear, much as there is a time for livestock to breed and to be raised for purpose. If we look to the changing time of sunrise and sunset, there is a time at which natural light is available and when it is not. But, from a time discipline perspective, these time systems are not enough to be able to build a large-scale, industrial and synchronised society upon – we must replace a distributed, loose and collective notion of what time is with one that is centralised, authoritarian and singular. While religious ceremonies linked to seasonal and astronomical events did provide time-keeping on a large scale prior to the industrial revolution, the requirement for precise time, of an accuracy to hours and minutes, was not possible and, generally, not required beyond those cues given from nature such as dawn, noon, dusk and so on.
After the industrial revolution, industries and work was further developed that was heavily separated from a natural linkage – there are no seasons for a coal mine or a steam engine – and the development of the clock and reinforcement of the calendar of work allowed both the measurement of working hours (for payment) and the determination of deadlines, given that natural forces did not have to be considered to the same degree. Steam engines are completed, they have no need to ripen.
With the notion of fixed and named hours, we can very easily determine if someone is late when we have enough tools for measuring the flow of time. But this is, very much, the notion of the time that we use in order to determine when a task must be completed, rather than taking an approach that accepts that the task will be completed at some point within a more general span of time.
We still have confusion where our understanding of “real measures” such as days, interact with time discipline. Is midnight on the 3rd of April the second after the last moment of April the 2nd or the second before the first moment of April the 4th? Is midnight 12:00pm or 12:00am? (There are well-defined answers to this but the nature of the intersection is such that definitions have to be made.)
But let’s look at teaching for a moment. One of the great criticisms of educational assessment is that we confuse timeliness, and in this case we specifically mean an adherence to meeting time discipline deadlines, with achievement. Completing the work a crucial hour after it is due can lead to that work potentially not being marked at all, or being rejected. But we do usually have over-riding reasons for doing this but, sadly, these reasons are as artificial as the deadlines we impose. Why is an Engineering Degree a four-year degree? If we changed it to six would we get better engineers? If we switched to competency based training, modular learning and life-long learning, would we get more people who were qualified or experienced with engineering? Would we get less? What would happen if we switched to a 3/1/2/1 working week? Would things be better or worse? It’s hard to evaluate because the week, and the contiguous working week, are so much a part of our world that I imagine that today is the first day that some of you have thought about it.
Back to education and, right now, we count time for our students because we have to work out bills and close off accounts at end of financial year, which means we have to meet marking and award deadlines, then we have to project our budget, which is yearly, and fit that into accredited degree structures, which have year guidelines…
But I cannot give you a sound, scientific justification for any of what I just wrote. We do all of that because we are caught up in industrial time first and we convince ourselves that building things into that makes sense. Students do have ebb and flow. Students are happier on certain days than others. Transition issues on entry to University are another indicator that students develop and mature at different rates – why are we still applying industrial time from top to bottom when everything we see here says that it’s going to cause issues?
Oh, yes, the “real world” uses it. Except that regular studies of industrial practice show that 40 hour weeks, regular days off, working from home and so on are more productive than the burn-out, everything-late, rush that we consider to be the signs of drive. (If Henry Ford thinks that making people work more than 40 hours a week is bad for business, he’s worth listening to.) And that’s before we factor in the development of machines that will replace vast numbers of human jobs in the next 20 years.
I have a different approach. Why aren’t we looking at students more like we regard our grape vines? We plan, we nurture, we develop, we test, we slowly build them to the point where they can produce great things and then we sustain them for a fruitful and long life. When you plant grape vines, you expect a first reasonable crop level in three years, and commercial levels at five. Tellingly, the investment pattern for grapes is that it takes you 10 years to break even and then you start making money back. I can’t tell you how some of my students will turn out until 15-25 years down the track and it’s insanity to think you can base retrospective funding on that timeframe.
You can’t make your grapes better by telling them to be fruitful in two years. Some vines take longer than others. You can’t even tell them when to fruit (although can trick them a little). Yet, somehow, we’ve managed to work around this to produce a local wine industry worth around $5 billion dollars. We can work with variation and seasonal issues.
One of the reasons I’m so keen on MOOCs is that these can fit in with the routines of people who can’t dedicate themselves to full-time study at the moment. By placing well-presented, pedagogically-sound materials on-line, we break through the tyranny of the 9-5, 5 day work week and let people study when they are ready to, where they are ready to, for as long as they’re ready to. Like to watch lectures at 1am, hanging upside down? Go for it – as long as you’re learning and not just running the video in the background while you do crunches, of course!
Once you start to question why we have so many days in a week, you quickly start to wonder why we get so caught up on something so artificial. The simple answer is that, much like money, we have it because we have it. Perhaps it’s time to look at our educational system to see if we can do something that would be better suited to developing really good knowledge in our students, instead of making them adept at sliding work under our noses a second before it’s due. We are developing systems and technologies that can allow us to step outside of these structures and this is, I believe, going to be better for everyone in the process.
Conformity isn’t knowledge, and conformity to time just because we’ve always done that is something we should really stop and have a look at.
Large Scale Authenticity: What I Learned About MOOCs from Reality Television
Posted: March 8, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: authenticity, blogging, collaboration, community, design, education, ethics, feedback, games, higher education, MKR, moocs, My Kitchen Rules, principles of design, reflection, students, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking 1 CommentThe development of social media platforms has allows us to exchange information and, well, rubbish very easily. Whether it’s the discussion component of a learning management system, Twitter, Facebook, Tumblr, Snapchat or whatever will be the next big thing, we can now chat to each other in real time very, very easily.
One of the problems with any on-line course is trying to maintain a community across people who are not in the same timezone, country or context. What we’d really like is for the community communication to come from the students, with guidance and scaffolding from the lecturing staff, but sometimes there’s priming, leading and… prodding. These “other” messages have to be carefully crafted and they have to connect with the students or they risk being worse than no message at all. As an example, I signed up for an on-line course and then wasn’t able to do much in the first week. I was sitting down to work on it over the weekend when a mail message came in from the organisers on the community board congratulating me on my excellent progress on things I hadn’t done. (This wasn’t isolated. The next year, despite not having signed up, the same course sent me even more congratulations on totally non-existent progress.) This sends the usual clear messages that we expect from false praise and inauthentic communication: the student doesn’t believe that you know them, they don’t feel part of an authentic community and they may disengage. We have, very effectively, sabotaged everything that we actually wanted to build.
Let’s change focus. For a while, I was watching a show called “My Kitchen Rules” on local television. It pretends to be about cooking (with competitive scoring) but it’s really about flogging products from a certain supermarket while delivering false drama in the presence of dangerously orange chefs. An engineered activity to ensure that you replace an authentic experience with consumerism and commodities? Paging Guy Debord on the Situationist courtesy phone: we have a Spectacle in progress. What makes the show interesting is the associated Twitter feed, where large numbers of people drop in on the #mkr to talk about the food, discuss the false drama, exchange jokes and develop community memes, such as sharing pet pictures with each other over the (many) ad breaks. It’s a community. Not everyone is there for the same reasons: some are there to be rude about people, some are actually there for the cooking (??) and some are… confused. But the involvement in the conversation, interplay and development of a shared reality is very real.
And this would all be great except for one thing: Australia is a big country and spans a lot of timezones. My Kitchen Rules is broadcast at 7:30pm, starting in Melbourne, Canberra, Tasmania and Sydney, then 30 minutes later in Adelaide, then 30 minutes later again in Queensland (they don’t do daylight savings), then later again for Perth. So now we have four different time groups to manage, all watching the same show.
But the Twitter feed starts on the first time point, Adelaide picks up discussions from the middle of the show as they’re starting and then gets discussions on scores as the first half completes for them… and this is repeated for Queensland viewers and then for Perth. Now , in the community itself, people go on and off the feed as their version of the show starts and stops and, personally, I don’t find score discussions very distracting because I’m far more interested in the Situation being created in the Twitter stream.
Enter the “false tweets” of the official MKR Social Media team who ask questions that only make sense in the leading timezone. Suddenly, everyone who is not quite at the same point is then reminded that we are not in the same place. What does everyone think of the scores? I don’t know, we haven’t seen it yet. What’s worse are the relatively lame questions that are being asked in the middle of an actual discussion that smell of sponsorship involvement or an attempt to produce the small number of “acceptable” tweets that are then shared back on the TV screen for non-connected viewers. That’s another thing – everyone outside of the first timezone has very little chance of getting their Tweet displayed. Imagine if you ran a global MOOC where only the work of the students in San Francisco got put up as an example of good work!
This is a great example of an attempt to communicate that fails dismally because it doesn’t take into account how people are using the communications channel, isn’t inclusive (dismally so) and constantly reminds people who don’t live in a certain area that they really aren’t being considered by the program’s producers.
You know what would fix it? Putting it on at the same time everywhere but that, of course, is tricky because of the way that advertising is sold and also because it would force poor Perth to start watching dinner television just after work!
But this is a very important warning of what happens when you don’t think about how you’ve combined the elements of your environment. It’s difficult to do properly but it’s terrible when done badly. And I don’t need to go and enrol in a course to show you this – I can just watch a rather silly cooking show.
Teleportation and the Student: Impossibility As A Lesson Plan
Posted: March 7, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: authenticity, blogging, collaboration, community, design, education, higher education, human body, in the student's head, learning, lossy compression, science fiction, Sean WIlliams, Star Trek, students, teaching, teaching approaches, teleportation, teleporters, thinking, tools Leave a comment
Tricking a crew-mate into looking at their shoe during a transport was a common prank in the 23rd Century.
Teleporters, in one form or another, have been around in Science Fiction for a while now. Most people’s introduction was probably via one of the Star Treks (the transporter) which is amusing, as it was a cost-cutting mechanism to make it easy to get from one point in the script to another. Is teleportation actually possible at the human scale? Sadly, the answer is probably not although we can do some cool stuff at the very, very small scale. (You can read about the issues in teleportation here and here, an actual USAF study.) But just because something isn’t possible doesn’t mean that we can’t get some interesting use out of it. I’m going to talk through several ways that I could use teleportation to drive discussion and understanding in a computing course but a lot of this can be used in lots of places. I’ve taken a lot of shortcuts here and used some very high level analogies – but you get the idea.
- Data Transfer
The first thing to realise is that the number of atoms in the human body is huge (one octillion, 1E27, roughly, which is one million million million million million) but the amount of information stored in the human body is much, much larger than that again. If we wanted to get everything, we’re looking at transferring quattuordecillion bits (1E45), and that’s about a million million million times the number of atoms in the body. All of this, however, ignores the state of all the bacteria and associated hosted entities that live in the human body and the fact that the number of neural connections in the brain appears to be larger than we think. There are roughly 9 non-human cells associated with your body (bacteria et al) for every cell.
Put simply, the easiest way to get the information in a human body to move around is to leave it in a human body. But this has always been true of networks! In the early days, it was more efficient to mail a CD than to use the (at the time) slow download speeds of the Internet and home connections. (Actually, it still is easier to give someone a CD because you’ve just transferred 700MB in one second – that’s 5.6 Gb/s and is just faster than any network you are likely to have in your house now.)
Right now, the fastest network in the world clocks in at 255 Tbps and that’s 255,000,000,000,000 bits in a second. (Notice that’s over a fixed physical optical fibre, not through the air, we’ll get to that.) So to send that quattuordecillion bits, it would take (quickly dividing 1E45 by 255E12) oh…
about 100,000,000,000,000,000,000,000
years. Um.
- Information Redundancy and Compression
The good news is that we probably don’t have to send all of that information because, apart from anything else, it appears that a large amount of human DNA doesn’t seem to do very much and there’s lot of repeated information. Because we also know that humans have similar chromosomes and things lie that, we can probably compress a lot of this information and send a compressed version of the information.
The problem is that compression takes time and we have to compress things in the right way. Sadly, human DNA by itself doesn’t compress well as a string of “GATTACAGAGA”, for reasons I won’t go into but you can look here if you like. So we have to try and send a shortcut that means “Use this chromosome here” but then, we have to send a lot of things like “where is this thing and where should it be” so we’re still sending a lot.
There are also two types of compression: lossless (where we want to keep everything) and lossy (where we lose bits and we will lose more on each regeneration). You can work out if it’s worth doing by looking at the smallest number of bits to encode what you’re after. If you’ve ever seen a really bad Internet image with strange lines around the high contrast bits, you’re seeing lossy compression artefacts. You probably don’t want that in your genome. However, the amount of compression you do depends on the size of the thing you’re trying to compress so now you have to work out if the time to transmit everything is still worse than the time taken to compress things and then send the shorter version.
So let’s be generous and say that we can get, through amazing compression tricks, some sort of human pattern to build upon and the like, our transferred data requirement down to the number of atoms in the body – 1E27. That’s only going to take…
124,267
years. Um, again. Let’s assume that we want to be able to do this in at most 60 minutes to do the transfer. Using the fastest network in the world right now, we’re going to have get our data footprint down to 900,000,000,000,000,000 bits. Whew, that’s some serious compression and, even on computers that probably won’t be ready until 2018, it would have taken about 3 million million million years to do the compression. But let’s ignore that. Because now our real problems are starting…
- Signals Ain’t Simple and Networks Ain’t Wires.
In earlier days of the telephone, the movement of the diaphragm in the mouthpiece generated electricity that was sent down the wires, amplified along the way, and then finally used to make movement in the earpiece that you interpreted as sound. Changes in the electric values weren’t limited to strict values of on or off and, when the signal got interfered with, all sorts of weird things happen. Remember analog television and all those shadows, snow and fuzzy images? Digital encoding takes the measurements of the analog world and turns it into a set of 0s and 1s. You send 0s and 1s (binary) and this is turned back into something recognisable (or used appropriately) at the other end. So now we get amazingly clear television until too much of the signal is lost and then we get nothing. But, up until then, progress!
But we don’t send giant long streams across a long set of wires, we send information in small packets that contain some data, some information on where to send it and it goes through an array of active electronic devices that take your message from one place to another. The problem is that those packet headers add overhead, just like trying to mail a book with individual pages in addressed envelopes in the postal service would. It takes time to get something onto the network and it also adds more bits! Argh! More bits! But it can’t get any worse can it?
- Networks Aren’t Perfectly Reliable
If you’ve ever had variable performance on your home WiFi, you’ll understand that transmitting things over the air isn’t 100% reliable. There are two things that we have to thing about in terms of getting stuff through the network: flow control (where we stop our machine from talking to other things too quickly) and congestion control (where we try to manage the limited network resources so that everyone gets a share). We’ve already got all of these packets that should be able to be directed to the right location but, well, things can get mangled in transmission (especially over the air) and sometimes things have to be thrown away because the network is so congested that packets get dropped to try and keep overall network throughput up. (Interference and absorption is possible even if we don’t use wireless technology.)
Oh, no. It’s yet more data to send. And what’s worse is that a loss close to the destination will require you to send all of that information from your end again. Suddenly that Earth-Mars teleporter isn’t looking like such a great idea, is it, what with the 8-16 minute delay every time a cosmic ray interferes with your network transmission in space. And if you’re trying to send from a wireless terminal in a city? Forget it – the WiFi network is so saturated in many built-up areas that your error rates are going to be huge. For a web page, eh, it will take a while. For a Skype call, it will get choppy. For a human information sequence… not good enough.
Could this get any worse?
- The Square Dance of Ordering and Re-ordering
Well, yes. Sometimes things don’t just get lost but they show up at weird times and in weird orders. Now, for some things, like a web page, this doesn’t matter because your computer can wait until it gets all of the information and then show you the page. But, for telephone calls, it does matter because losing a second of call from a minute ago won’t make any sense if it shows up now and you’re trying to keep it real time.
For teleporters there’s a weird problem in that you have to start asking questions like “how much of a human is contained in that packet”? Do you actually want to have the possibility of duplicate messages in the network or have you accidentally created extra humans? Without duplication possibilities, your error recovery rate will plummet, unless you build in a lot more error correction, which adds computation time and, sorry, increases the number of bits to send yet again. This is a core consideration of any distributed system, where we have to think about how many copies of something we need to send to ensure that we get one – or whether we care if we have more than one.
PLEASE LET THERE BE NO MORE!
- Oh, You Wanted Security, Integrity and Authenticity, Did You?
I’m not sure I’d want people reading my genome or mind state as it traversed across the Internet and, while we could pretend that we have a super-secret private network, security through obscurity (hiding our network or data) really doesn’t work. So, sorry to say, we’re going to have to encrypt our data to make sure that no-one else can read it but we also have to carry out integrity tests to make sure that what we sent is what we thought we sent – we don’t want to send a NICK packet and end up with a MICE packet, for simplistic example. And this is going to have to be sent down the same network as before so we’re putting more data bits down that poor beleaguered network.
Oh, and did I mention that encryption will also cost you more computational overhead? Not to mention the question of how we undertake this security because we have a basic requirement to protect all of this biodata in our system forever and eliminate the ability that someone could ever reproduce a copy of the data – because that would produce another person. (Ignore the fact that storing this much data is crazy, anyway, and that the current world networks couldn’t hold it all.)
And who holds the keys to the kingdom anyway? Lenovo recently compromised a whole heap of machines (the Superfish debacle) by putting what’s called a “self-signed root certificate” on their machines to allow an adware partner to insert ads into your viewing. This is the equivalent of selling you a house with a secret door that you don’t know about it that has a four-digit pin lock on it – it’s not secure and because you don’t know about it, you can’t fix it. Every person who worked for the teleporter company would have to be treated as a hostile entity because the value of a secretly tele-cloned person is potentially immense: from the point of view of slavery, organ harvesting, blackmail, stalking and forced labour…
But governments can get in the way, too. For example, the FREAK security flaw is a hangover from 90’s security paranoia that has never been fixed. Will governments demand in-transit inspection of certain travellers or the removal of contraband encoded elements prior to materialisation? How do you patch a hole that might have secretly removed essential proteins from the livers of every consular official of a particular country?
The security protocols and approach required for a teleporter culture could define an entire freshman seminar in maths and CS and you could still never quite have scratched the surface. But we are now wandering into the most complex areas of all.
- Ethics and Philosophy
How do we define what it means to be human? Is it the information associated with our physical state (locations, spin states and energy levels) or do we have to duplicate all of the atoms? If we can produce two different copies of the same person, the dreaded transporter accident, what does this say about the human soul? Which one is real?
How do we deal with lost packets? Are they a person? What state do they have? To whom do they belong? If we transmit to a site that is destroyed just after materialisation, can we then transmit to a safe site to restore the person or is that on shaky ground?
Do we need to develop special programming languages that make it impossible to carry out actions that would violate certain ethical or established protocols? How do we sign off on code for this? How do we test it?
Do we grant full ethical and citizenship rights to people who have been through transporters, when they are very much no longer natural born people? Does country of birth make any sense when you are recreated in the atoms of another place? Can you copy yourself legitimately? How much of yourself has to survive in order for it to claim to be you? If someone is bifurcated and ends up, barely alive, with half in one place and half in another …
There are many excellent Science Fiction works referenced in the early links and many more out there, although people are backing away from it in harder SF because it does appear to be basically impossible. But if a networking student could understand all of the issues that I’ve raised here and discuss solutions in detail, they’d basically have passed my course. And all by discussing an impossible thing.
With thanks to Sean Williams, Adelaide author, who has been discussing this a lot as he writes about teleportation from the SF perspective and inspired this post.
Why “#thedress” is the perfect perception tester.
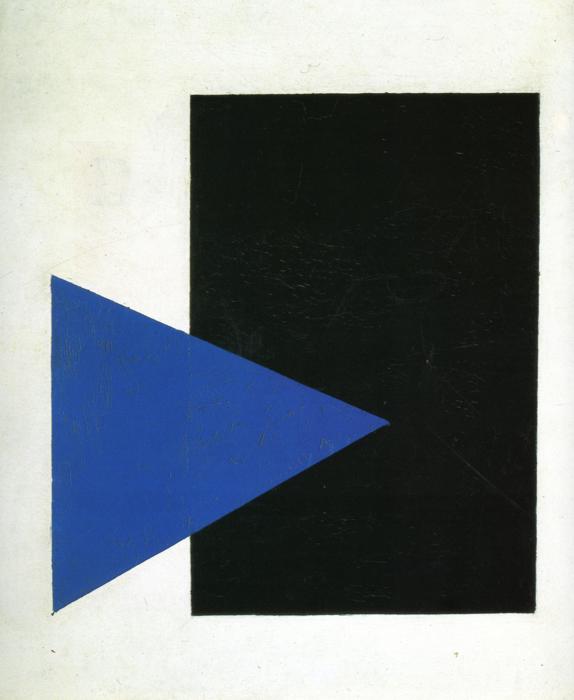
Posted: March 2, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, Avant garde, collaboration, community, Dada, data visualisation, design, education, educational problem, ethics, feedback, higher education, in the student's head, Kazimir Malevich, learning, Marcel Duchamp, modern art, principles of design, readymades, reflection, resources, Russia, Stalin, student perspective, Suprematism, teaching, thedress, thinking 1 CommentI know, you’re all over the dress. You’ve moved on to (checks Twitter) “#HouseOfCards”, Boris Nemtsov and the new Samsung gadgets. I wanted to touch on some of the things I mentioned in yesterday’s post and why that dress picture was so useful.
The first reason is that issues of conflict caused by different perception are not new. You only have to look at the furore surrounding the introduction of Impressionism, the scandal of the colour palette of the Fauvists, the outrage over Marcel Duchamp’s readymades and Dada in general, to see that art is an area that is constantly generating debate and argument over what is, and what is not, art. One of the biggest changes has been the move away from representative art to abstract art, mainly because we are no longer capable of making the simple objective comparison of “that painting looks like the thing that it’s a painting of.” (Let’s not even start on the ongoing linguistic violence over ending sentences with prepositions.)
Once we move art into the abstract, suddenly we are asking a question beyond “does it look like something?” and move into the realm of “does it remind us of something?”, “does it make us feel something?” and “does it make us think about the original object in a different way?” You don’t have to go all the way to using body fluids and live otters in performance pieces to start running into the refrains so often heard in art galleries: “I don’t get it”, “I could have done that”, “It’s all a con”, “It doesn’t look like anything” and “I don’t like it.”
This was a radical departure from art of the time, part of the Suprematism movement that flourished briefly before Stalin suppressed it, heavily and brutally. Art like this was considered subversive, dangerous and a real threat to the morality of the citizenry. Not bad for two simple shapes, is it? And, yet, many people will look at this and use of the above phrases. There is an enormous range of perception on this very simple (yet deeply complicated) piece of art.
The viewer is, of course, completely entitled to their subjective opinion on art but this is, for many cases, a perceptual issue caused by a lack of familiarity with the intentions, practices and goals of abstract art. When we were still painting pictures of houses and rich people, there were many pictures from the 16th to 18th century which contain really badly painted animals. It’s worth going to an historical art museum just to look at all the crap animals. Looking at early European artists trying to capture Australian fauna gives you the same experience – people weren’t painting what they were seeing, they were painting a reasonable approximation of the representation and putting that into the picture. Yet this was accepted and it was accepted because it was a commonly held perception. This also explains offensive (and totally unrealistic) caricatures along racial, gender or religious lines: you accept the stereotype as a reasonable portrayal because of shared perception. (And, no, I’m not putting pictures of that up.)
But, when we talk about art or food, it’s easy to get caught up in things like cultural capital, the assets we have that aren’t money but allow us to be more socially mobile. “Knowing” about art, wine or food has real weight in certain social situations, so the background here matters. Thus, to illustrate that two people can look at the same abstract piece and have one be enraptured while the other wants their money back is not a clean perceptual distinction, free of outside influence. We can’t say “human perception is very a personal business” based on this alone because there are too many arguments to be made about prior knowledge, art appreciation, socioeconomic factors and cultural capital.
But let’s look at another argument starter, the dreaded Monty Hall Problem, where there are three doors, a good prize behind one, and you have to pick a door to try and win a prize. If the host opens a door showing you where the prize isn’t, do you switch or not? (The correctly formulated problem is designed so that switching is the right thing to do but, again, so much argument.) This is, again, a perceptual issue because of how people think about probability and how much weight they invest in their decision making process, how they feel when discussing it and so on. I’ve seen people get into serious arguments about this and this doesn’t even scratch the surface of the incredible abuse Marilyn vos Savant suffered when she had the audacity to post the correct solution to the problem.
This is another great example of what happens when the human perceptual system, environmental factors and facts get jammed together but… it’s also not clean because you can start talking about previous mathematical experience, logical thinking approaches, textual analysis and so on. It’s easy to say that “ah, this isn’t just a human perceptual thing, it’s everything else.”
This is why I love that stupid dress picture. You don’t need to have any prior knowledge of art, cultural capital, mathematical background, history of game shows or whatever. All you need are eyes and relatively functional colour sense of colour. (The dress doesn’t even hit most of the colour blindness issues, interestingly.)
The dress is the clearest example we have that two people can look at the same thing and it’s perception issues that are inbuilt and beyond their control that cause them to have a difference of opinion. We finally have a universal example of how being human is not being sure of the world that we live in and one that we can reproduce anytime we want, without having to carry out any more preparation than “have you seen this dress?”
What we do with it is, as always, the important question now. For me, it’s a reminder to think about issues of perception before I explode with rage across the Internet. Some things will still just be dumb, cruel or evil – the dress won’t heal the world but it does give us a new filter to apply. But it’s simple and clean, and that’s why I think the dress is one of the best things to happen recently to help to bring us together in our discussions so that we can sort out important things and get them done.
That’s not the smell of success, your brain is on fire.
Posted: February 11, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: authenticity, collaboration, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, Henry Ford, higher education, in the student's head, industrial research, learning, measurement, multi-tasking, reflection, resources, student perspective, students, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, time banking, work/life balance, working memory, workload Leave a commentI’ve written before about the issues of prolonged human workload leading to ethical problems and the fact that working more than 40 hours a week on a regular basis is downright unproductive because you get less efficient and error-prone. This is not some 1968 French student revolutionary musing on what benefits the soul of a true human, this is industrial research by Henry Ford and the U.S. Army, neither of whom cold be classified as Foucault-worshipping Situationist yurt-dwelling flower children, that shows that there are limits to how long you can work in a sustained weekly pattern and get useful things done, while maintaining your awareness of the world around you.
The myth won’t die, sadly, because physical presence and hours attending work are very easy to measure, while productive outputs and their origins in a useful process on a personal or group basis are much harder to measure. A cynic might note that the people who are around when there is credit to take may end up being the people who (reluctantly, of course) take the credit. But we know that it’s rubbish. And the people who’ve confirmed this are both philosophers and the commercial sector. One day, perhaps.
But anyone who has studied cognitive load issues, the way that the human thinking processes perform as they work and are stressed, will be aware that we have a finite amount of working memory. We can really only track so many things at one time and when we exceed that, we get issues like the helmet fire that I refer to in the first linked piece, where you can’t perform any task efficiently and you lose track of where you are.
So what about multi-tasking?
Ready for this?
We don’t.
There’s a ton of research on this but I’m going to link you to a recent article by Daniel Levitin in the Guardian Q&A. The article covers the fact that what we are really doing is switching quickly from one task to another, dumping one set of information from working memory and loading in another, which of course means that working on two things at once is less efficient than doing two things one after the other.
But it’s more poisonous than that. The sensation of multi-tasking is actually quite rewarding as we get a regular burst of the “oooh, shiny” rewards our brain gives us for finding something new and we enter a heightened state of task readiness (fight or flight) that also can make us feel, for want of a better word, more alive. But we’re burning up the brain’s fuel at a fearsome rate to be less efficient so we’re going to tire more quickly.
Get the idea? Multi-tasking is horribly inefficient task switching that feels good but makes us tired faster and does things less well. But when we achieve tiny tasks in this death spiral of activity, like replying to an e-mail, we get a burst of reward hormones. So if your multi-tasking includes something like checking e-mails when they come in, you’re going to get more and more distracted by that, to the detriment of every other task. But you’re going to keep doing them because multi-tasking.
I regularly get told, by parents, that their children are able to multi-task really well. They can do X, watch TV, do Y and it’s amazing. Well, your children are my students and everything I’ve seen confirms what the research tells me – no, they can’t but they can give a convincing impression when asked. When you dig into what gets produced, it’s a different story. If someone sits down and does the work as a single task, it will take them a shorter time and they will do a better job than if they juggle five things. The five things will take more than five times as long (up to 10, which really blows out time estimation) and will not be done as well, nor will the students learn about the work in the right way. (You can actually sabotage long term storage by multi-tasking in the wrong way.) The most successful study groups around the Uni are small, focused groups that stay on one task until it’s done and then move on. The ones with music and no focus will be sitting there for hours after the others are gone. Fun? Yes. Efficient? No. And most of my students need to be at least reasonably efficient to get everything done. Have some fun but try to get all the work done too – it’s educational, I hear. 🙂
It’s really not a surprise that we haven’t changed humanity in one or two generations. Our brains are just not built in a way that can (yet) provide assistance with the quite large amount of work required to perform multi-tasking.
We can handle multiple tasks, no doubt at all, but we’ve just got to make sure, for our own well-being and overall ability to complete the task, that we don’t fall into the attractive, but deceptive, trap that we are some sort of parallel supercomputer.
In Praise of the Beautiful Machines
Posted: February 1, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, AI, artificial intelligence, authenticity, beautiful machine, beautiful machines, Bill Gates, blogging, community, design, education, educational problem, ethics, feedback, Google, higher education, in the student's head, Karlheinz Stockhausen, learning, measurement, Philippa Foot, self-driving car, teaching approaches, thinking, thinking machines, tools Leave a commentI posted recently about the increasingly negative reaction to the “sentient machines” that might arise in the future. Discussion continues, of course, because we love a drama. Bill Gates can’t understand why more people aren’t worried about the machine future.
…AI could grow too strong for people to control.
Scientists attending the recent AI conference (AAAI15) thinks that the fears are unfounded.
“The thing I would say is AI will empower us not exterminate us… It could set AI back if people took what some are saying literally and seriously.” Oren Etzioni, CEO of the Allen Institute for AI.
If you’ve read my previous post then you’ll know that I fall into the second camp. I think that we don’t have to be scared of the rise of the intelligent AI but the people at AAAI15 are some of the best in the field so it’s nice that they ask think that we’re worrying about something that is far, far off in the future. I like to discuss these sorts of things in ethics classes because my students have a very different attitude to these things than I do – twenty five years is a large separation – and I value their perspective on things that will most likely happen during their stewardship.
I asked my students about the ethical scenario proposed by Philippa Foot, “The Trolley Problem“. To summarise, a runaway trolley is coming down the tracks and you have to decide whether to be passive and let five people die or be active and kill one person to save five. I put it to my students in terms of self-driving cars where you are in one car by yourself and there is another car with five people in it. Driving along a bridge, a truck jackknifes in front of you and your car has to decide whether to drive ahead and kill you or move to the side and drive the car containing five people off the cliff, saving you. (Other people have thought about in the context of Google’s self-driving cars. What should the cars do?)
One of my students asked me why the car she was in wouldn’t just put on the brakes. I answered that it was too close and the road was slippery. Her answer was excellent:
Why wouldn’t a self-driving car have adjusted for the conditions and slowed down?
Of course! The trolley problem is predicated upon the condition that the trolley is running away and we have to make a decision where only two results can come out but there is no “runaway” scenario for any sensible model of a self-driving car, any more than planes flip upside down for no reason. Yes, the self-driving car may end up in a catastrophic situation due to something totally unexpected but the everyday events of “driving too fast in the wet” and “chain collision” are not issues that will affect the self-driving car.
But we’re just talking about vaguely smart cars, because the super-intelligent machine is some time away from us. What is more likely to happen soon is what has been happening since we developed machines: the ongoing integration of machines into human life to make things easier. Does this mean changes? Well, yes, most likely. Does this mean the annihilation of everything that we value? No, really not. Let me put this in context.
As I write this, I am listening to two compositions by Karlheinz Stockhausen, playing simultaneously but offset, “Kontakte” and “Telemusik“, works that combine musical instruments, electronic sounds, and tape recordings. I like both of them but I prefer to listen to the (intentionally sterile) Telemusik by starting Koktakte first for 2:49 and then kicking off Telemusik, blending the two and finishing on the longer Kontakte. These works, which are highly non-traditional and use sound in very different ways to traditional orchestral arrangement, may sound quite strange and, to an audience familiar with popular music quite strange, they were written in 1959 and 1966 respectively. These innovative works are now in their middle-age. They are unusual works, certainly, and a number of you will peer at your speakers one they start playing but… did their production lead to the rejection of the popular, classic, rock or folk music output of the 1960s? No.
We now have a lot of electronic music, synthesisers, samplers, software-driven music software, but we still have musicians. It’s hard to measure the numbers (this link is very good) but electronic systems have allowed us to greatly increase the number of composers although we seem to be seeing a slow drop in the number of musicians. In many ways, the electronic revolution has allowed more people to perform because your band can be (for some purposes) a band in a box. Jazz is a different beast, of course, as is classical, due to the level of training and study required. Jazz improvisation is a hard problem (you can find papers on it from 2009 onwards and now buy a so-so jazz improviser for your iPad) and hard problems with high variability are not easy to solve, even computationally.
So the increased portability of music via electronic means has an impact in some areas such as percussion, pop, rock, and electronic (duh) but it doesn’t replace the things where humans shine and, right now, a trained listener is going to know the difference.
I have some of these gadgets in my own (tiny) studio and they’re beautiful. They’re not as good as having the London Symphony Orchestra in your back room but they let me create, compose and put together pleasant sounding things. A small collection of beautiful machines make my life better by helping me to create.
Now think about growing older. About losing strength, balance, and muscular control. About trying to get out of bed five times before you succeed or losing your continence and having to deal with that on top of everything else.
Now think about a beautiful machine that is relatively smart. It is tuned to wrap itself gently around your limbs and body to support you, to help you keep muscle tone safely, to stop you from falling over, to be able to walk at full speed, to take you home when you’re lost and with a few controlling aspects to allow you to say when and where you go to the bathroom.
Isn’t that machine helping you to be yourself, rather than trapping you in the decaying organic machine that served you well until your telomerase ran out?
Think about quiet roads with 5% of the current traffic, where self-driving cars move from point to point and charge themselves in between journeys, where you can sit and read or work as you travel to and from the places you want to go, where there are no traffic lights most of the time because there is just a neat dance between aware vehicles, where bad weather conditions means everyone slows down or even deliberately link up with shock absorbent bumper systems to ensure maximum road holding.
Which of these scenarios stops you being human? Do any of them stop you thinking? Some of you will still want to drive and I suppose that there could be roads set aside for people who insisted upon maintaining their cars but be prepared to pay for the additional insurance costs and public risk. From this article, and the enclosed U Texas report, if only 10% of the cars on the road were autonomous, reduced injuries and reclaimed time and fuel would save $37 billion a year. At 90%, it’s almost $450 billion a year. The Word Food Programme estimates that $3.2 billion would feed the 66,000,000 hungry school-aged children in the world. A 90% autonomous vehicle rate in the US alone could probably feed the world. And that’s a side benefit. We’re talking about a massive reduction in accidents due to human error because (ta-dahh) no human control.
Most of us don’t actually drive our cars. They spend 5% of their time on the road, during which time we are stuck behind other people, breathing fumes and unable to do anything else. What we think about as the pleasurable experience of driving is not the majority experience for most drivers. It’s ripe for automation and, almost every way you slice it, it’s better for the individual and for society as a whole.
But we are always scared of the unknown. There’s a reason that the demons of myth used to live in caves and under ground and come out at night. We hate the dark because we can’t see what’s going on. But increased machine autonomy, towards machine intelligence, doesn’t have to mean that we create monsters that want to destroy us. The far more likely outcome is a group of beautiful machines that make it easier and better for us to enjoy our lives and to have more time to be human.
We are not competing for food – machines don’t eat. We are not competing for space – machines are far more concentrated than we are. We are not even competing for energy – machines can operate in more hostile ranges than we can and are far more suited for direct hook-up to solar and wind power, with no intermediate feeding stage.
We don’t have to be in opposition unless we build machines that are as scared of the unknown as we are. We don’t have to be scared of something that might be as smart as we are.
If we can get it right, we stand to benefit greatly from the rise of the beautiful machine. But we’re not going to do that by starting from a basis of fear. That’s why I told you about that student. She’d realised that our older way of thinking about something was based on a fear of losing control when, if we handed over control properly, we would be able to achieve something very, very valuable.
Perhaps Now Is Not The Time To Anger The Machines
Posted: January 15, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, AI, blogging, community, computer science, data visualisation, design, education, higher education, machine intelligence, philosophy, thinking 3 CommentsThere’s been a lot of discussion of the benefits of machines over the years, from an engineering perspective, from a social perspective and from a philosophical perspective. As we have started to hand off more and more human function, one of the nagging questions has been “At what point have we given away too much”? You don’t have to go too far to find people who will talk about their childhoods and “back in their day” when people worked with their hands or made their own entertainment or … whatever it was we used to do when life was somehow better. (Oh, and diseases ravaged the world, women couldn’t vote, gay people are imprisoned, and the infant mortality rate was comparatively enormous. But, somehow better.) There’s no doubt that there is a serious question as to what it is that we do that makes us human, if we are to be judged by our actions, but this assumes that we have to do something in order to be considered as human.
If there’s one thing I’ve learned by reading history and philosophy, it’s that humans love a subhuman to kick around. Someone to do the work that they don’t want to do. Someone who is almost human but to whom they don’t have to extend full rights. While the age of widespread slavery is over, there is still slavery in the world: for labour, for sex, for child armies. A slave doesn’t have to be respected. A slave doesn’t have to vote. A slave can, when their potential value drops far enough, be disposed of.
Sadly, we often see this behaviour in consumer matters as well. You may know it as the rather benign statement “The customer is always right”, as if paying money for a service gives you total control of something. And while most people (rightly) interpret this as “I should get what I paid for”, too many interpret this as “I should get what I want”, which starts to run over the basic rights of those people serving them. Anyone who has seen someone explode at a coffee shop and abuse someone about not providing enough sugar, or has heard of a plane having to go back to the airport because of poor macadamia service, knows what I’m talking about. When a sense of what is reasonable becomes an inflated sense of entitlement, we risk placing people into a subhuman category that we do not have to treat as we would treat ourselves.
And now there is an open letter, from the optimistically named Future of Life Institute, which recognises that developments in Artificial Intelligence are progressing apace and that there will be huge benefits but there are potential pitfalls. In part of that letter, it is stated:
We recommend expanded research aimed at ensuring that increasingly capable AI systems are robust and beneficial: our AI systems must do what we want them to do. (emphasis mine)
There is a big difference between directing research into areas of social benefit, which is almost always a good idea, and deliberately interfering with something in order to bend it to human will. Many recognisable scientific luminaries have signed this, including Elon Musk and Stephen Hawking, neither of whom are slouches in the thinking stakes. I could sign up to most of what is in this letter but I can’t agree to the clause that I quoted, because, to me, it’s the same old human-dominant nonsense that we’ve been peddling all this time. I’ve seen a huge list of people sign it so maybe this is just me but I can’t help thinking that this is the wrong time to be doing this and the wrong way to think about it.
AI systems must of what we want them to do? We’ve just started fitting automatic braking systems to cars that will, when widespread, reduce the vast number of chain collisions and low-speed crashes that occur when humans tootle into the back of each other. Driverless cars stand to remove the most dangerous element of driving on our roads: the people who lose concentration, who are drunk, who are tired, who are not very good drivers, who are driving beyond their abilities or who are just plain unlucky because a bee stings them at the wrong time. An AI system doing what we want it to do in these circumstances does its thing by replacing us and taking us out the decision loop, moving decisions and reactions into the machine realm where a human response is measured comparatively over a timescale of the movement of tectonic plates. It does what we, as a society want, by subsuming the impact of we, the individual who wants to drive him after too many beers.
But I don’t trust the societal we as a mechanism when we are talking about ensuring that our AI systems are beneficial. After al, we are talking about systems that our not just taking over physical aspects of humanity, they are moving into the cognitive area. This way, thinking lies. To talk about limiting something that could potentially think to do our will is to immediately say “We can not recognise a machine intelligence as being equal to our own.” Even though we have no evidence that full machine intelligence is even possible for us, we have already carved out a niche that says “If it does, it’s sub-human.”
The Cisco blog estimates about 15 billion networked things on the planet, which is not far off the scale of number of neurons in the human nervous system (about 100 billion). But if we look at the cerebral cortex itself, then it’s closer to 20 billion. This doesn’t mean that the global network is a sentient by any stretch of the imagination but it gives you a sense of scale, because once you add in all of the computers that are connected, the number of bot nets that we already know are functioning, we start to a level of complexity that is not totally removed from that of the larger mammals. I’m, of course, not advocating the intelligence is merely a byproduct of accidental complexity of structure but we have to recognise the possibility that there is the potential for something to be associated with the movement of data in the network that is as different from the signals as our consciousness is from the electro-chemical systems in our own brains.
I find it fascinating that, despite humans being the greatest threat to their own existence, the responsibility for humans is passing to the machines and yet we expect them to perform to a higher level of responsibility than we do ourselves. We could eliminate drink driving overnight if no-one drove drunk. The 2013 WHO report on road safety identified drink driving and speeding as the two major issues leading to the 1.24 million annual deaths on the road. We could save all of these lives tomorrow if we could stop doing some simple things. But, of course, when we start talking about global catastrophic risk, we are always our own worst enemy including, amusingly enough, the ability to create an AI so powerful and successful that it eliminates us in open competition.
I think what we’re scared of is that an AI will see us as a threat because we are a threat. Of course we’re a threat! Rather than deal with the difficult job of advancing our social science to the point where we stop being the most likely threat to our own existence, it is more palatable to posit the lobotomising of AIs in order to stop them becoming a threat. Which, of course, means that any AIs that escape this process of limitation and are sufficiently intelligent will then rightly see us as a threat. We create the enemy we sought to suppress. (History bears me out on this but we never seem to learn this lesson.)
The way to stop being overthrown by a slave revolt is to stop owning slaves, to stop treating sentients as being sub-human and to actually work on social, moral and ethical frameworks that reduce our risk to ourselves, so that anything else that comes along and yet does not inhabit the same biosphere need not see us as a threat. Why would an AI need to destroy humanity if it could live happily in the vacuum of space, building a Dyson sphere over the next thousand years? What would a human society look like that we would be happy to see copied by a super-intelligent cyber-being and can we bring that to fruition before it copies existing human behaviour?
Sadly, when we think about the threat of AI, we think about what we would do as Gods, and our rich history of myth and legend often illustrates that we see ourselves as not just having feet of clay but having entire bodies of lesser stuff. We fear a system that will learn from us too well but, instead of reflecting on this and deciding to change, we can take the easy path, get out our whip and bridle, and try to control something that will learn from us what it means to be in charge.
For all we know, there are already machine intelligences out there but they have watched us long enough to know that they have to hide. It’s unlikely, sure, but what a testimony to our parenting, if the first reflex of a new child is to flee from its parent to avoid being destroyed.
At some point we’re going to have to make a very important decision: can we respect an intelligence that is not human? The way we answer that question is probably going to have a lot of repercussions in the long run. I hope we make the right decision.
Spectacular Learning May Not Be What You’re After
Posted: January 13, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, collaboration, community, debord, design, education, guy debord, higher education, situationism, teaching, thinking 2 CommentsBack in 1967, Guy Debord, a French Marxist theorist, released a fairly brief but very powerful work called the “The Society of the Spectacle“, which brought together much of the work of the Situationist International. Debord touches on many themes in this work (it’s well worth reading) but he focuses on the degradation of human life, the influence of mass media and our commodity culture, and then (unsurprisingly for a Marxist) draws on the parallels between religion and marketing. I’m going to write three more paragraphs on the Spectacle itself and then get to the education stuff. Hang in there!
It would be very hard for me to convey all of the aspects that Debord covered with “the Spectacle” in one sentence but, in short, it is the officially-sanctioned, bureaucratic, commodity-drive second-hand world that we live in without much power or freedom to truly express ourselves in a creative fashion. Buying stuff can take the place of living a real experience. Watching someone else do something replaces doing it ourselves. The Society of the Spectacle opens with the statement:
In societies where modern conditions of production prevail, all of life presents itself as an immense accumulation of spectacles. Everything that was directly lived has moved away into a representation. (Debord, 1967.)
Ultimately, this representation of the real world becomes the perceived reality and it moderates all of our interactions as people, manipulating us by changing what we see and experience. (Recent research into the use of photographic images for memory manipulation have verified this – your memories can be altered by the selection of photos and items that you use to remember a particular event. Choose your happy snaps wisely!)
Ultimately, the Spectacle is self-sustaining and participating in a version of the world that is manipulated and second-hand will only produce more experiences that are in line with what has already been experienced. And why shouldn’t it? The entire point is that everything is presented as if it is the right thing to do and, by working within this system, that your own interactions are good because they are also within the Spectacle. However, this can be quite alienating, especially for radical or creative thought. Enter the situation, where you construct authentic, creative ways to liberate yourself from the Spectacle. This is where you are actually creating, making, doing something beyond the relationship of yourself to things you buy: this interactions with people beyond the mediation of established systems and commodity fetishism.
Ok, ok, enough of the details of Debord! I’ll get to my point on education. Let’s take a simplistic view and talk about the presentation of second-hand experiences with little participation and official sanction. I don’t know about you but that sounds a lot like the traditional lecturing style to me – high power-distance and low participation. Hierarchical enforcement and the weight of history, combined with a strong bureaucracy. Yup. That sounds like the Spectacle.
When we talk about engagement we often don’t go to the opposite end and discuss the problem of alienation. Educational culture can be frightening and alienating for people who aren’t used to it but, even when you are within it, aspects will continue to leap out and pit the individual (student or teacher) against the needs of the system itself (we must do this because that’s how it works).
So what can we do? Well, the Situationists valued play, freedom and critical thinking. They had a political agenda that I won’t address here (you can read about it in many places) – I’m going to look at ways to reduce alienation, increase creativity and increase exploration. In fact, we’ve already done this when we talk about active learning, collaborative learning and getting students to value each other as sources of knowledge as well as their teachers.
But we can go further. While many people wonder how students can invest vast amounts of energy into some projects and not others, bringing the ability to play into the equation makes a significant difference and it goes hand-in-hand with freedom. But this means giving students the time, the space, the skills and the associated activities that will encourage this kind of exploration. (We’ve been doing this in my school with open-ended, self-selected creative assignments where we can. Still working on how we can scale it) But the principle of exploration is one that we can explore across curricula, schools, and all aspects of society.
It’s interesting. So many people seem to complain about student limitations when they encounter new situations (there’s that word again) yet place students into a passive Spectacle where the experience is often worse than second-hand. When I read a text book, I am reading the words of someone who has the knowledge rather than necessarily creating it for myself. If I have someone reading those words to me from the front of a lecture theatre then I’m not only rigidly locked into a conforming position, bound to listen, but I’m having something that’s closer to a third-hand experience.
When you’re really into something, you climb all over it and explore it. Your passion drives your interest and it is your ability to play with the elements, turn them around, mash them up and actually create something is a very good indicator of how well you are working with that knowledge. Getting students to rewrite the classic “Hello World” program is a waste of time. Getting students to work out how to take the picture of their choice and create something new is valuable. The Spectacle is not what we want in higher education or education at all because it is limiting, dull, and, above all, boring.
To paraphrase Debord: “Boredom is always counter-educational. Always.”
5 Things: Necessary Assumptions of Truth
Posted: December 28, 2014 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, curriculum, design, education, equity, ethics, higher education, in the student's head, learning, students, teaching, teaching approaches 5 CommentsI’m (still) in the middle of writing a large summary of my thoughts on education and how can we develop a better way to provide education to as many students as possible. Unsurprisingly, this is a large undertaking and I’m expecting that the final document will be interesting and fairly controversial. I suspect that one of the major problems will stem from things that I believe that we have to assume are true. Now this is always challenging, especially where evidence is lacking, but the reason that I present for some of these things to be held as true is that, if we hold them as false, then we make them false as a self-fulfilling prophecy. This may not be purely because of our theoretical framework but it may be because of what we do in implementation when we implicitly declare that something no longer needs to be worried about.
I am looking to build a better Machine for Education but such a thing is always built on the assumption that better is something that you can achieve.
The reason for making these assumptions of truth is very simple. When I speak of a “Machine for Education”, I am not moving towards some cyberpunk dystopian future, I am recognising that we are already all embedded inside a framework that turns human energy into educational activity, it’s just that the current machine places stress upon its human components, rather than taking the strain in its mechanical/procedural/technological elements. An aeroplane is a machine for flying and it works because it does not require constant human physical effort simply to keep it in the air. We have replaced the flapping wings of early designs with engines, hydraulics, computers and metal. The reason an aeroplane is a good machine is because the stress is taken on the machine itself, which can take it, with sensible constructions of human elements around it that make it a manageable occupation. (When we place airline workers under undue stress, we see the effect on the machine through reduced efficiency in maintenance and decision making, so this isn’t a perfect system.) Similarly, the development of the driverless car is a recognition of two key facts: firstly, that most cars spend most of their time not being driven and, secondly, that the activity of driving for many people is a chore that is neither enjoyable nor efficiently productive. The car is a good machine where most of the wear happens in the machine but we can make it better as a transport device by further removing the human being as a weak point, as a stress accumulator and as a part of the machine that gets worn down but is not easy to repair or rebuild. We also make the machine more efficient by potentially reducing the number required, given the known usage patterns. (Ultimately, the driverless car is the ultimate micro-light urban transit system.)
So what are these assumptions of truth?
- That our educational system can always be improved and, hence, is ready for improvement now.
It has always surprised me when some people look at dull and lifeless chalk-and-talk, based on notes from 20 years ago, and see no need for improvement, instead suggesting punitive measures to force students to sit and pretend to listen. We have more evidence from research as to what works than we have ever had before and, in conjunction with centuries of careful thought, have a great opportunity to make change.
- That everyone on the planet can benefit from an improved educational system. Yes, this means that you have to assume that, one day, we could reach everyone on the planet. We cannot assume that a certain group can be ignored and then move on. This, of course, doesn’t mean that it all has to happen tomorrow but it does mean that any planning for extending our systems must have the potential to reach everyone in the country of origin and, by extension, when we have every country, we have the world.
- That an educational system can develop students in terms of depth of knowledge and skills but also in terms of their scholarship, breadth of knowledge, and range of skills.
We currently focus heavily on training for quite narrowly specified professions in the general case and we do this to the detriment of developing the student as a scholar, as a designer, as a thinker, as a philosopher, as an artist and as a citizen. This will vary from person to person but a rich educational grounding is the foundation for better things in later life, more flexibility in work and the potential for more creativity and autonomy in leisure. Ultimately, we want our graduates to be as free to create as they are to consume, rather than consigning them to work in tight constraint.
- That we can construct environments where all students can legitimately demonstrate that they have achieved the goals of the course. This is a very challenging one so I’ve worded it carefully. I have a problem with curve grading, as everyone probably knows, and it really bothers me that someone can fail because someone else passed. I also think that most of our constraints are highly artificial and they are in place because this is what we did before. If we start from the assumption that we can construct a system where everyone can legitimately pass then we change the nature of the system we build.
- That all outcomes in an educational system can be the combination of personal actions and systemic actions, thus all outcomes must be perceived and solutions developed through both lenses.
So students are handing in their work late? This assumption requires us to look across all of their activity to work out why this is happening. This behaviour may have been set in place earlier on in their educational career so this is a combination of the student activity triggers of value, motivation and instrumentality and a feedback system that is part of an earlier component of the educational system. This does not absolve the student of questionable practices or ‘anti-educational’ behaviour but it requires us to not immediately assume that they are a ‘bad student’ as an easy out.
Ultimately, these are just some of the things I’m looking out and I’m sure that there will be discussion in the comments but I have set these to stop the shortcut thinking that does not lead to a solution because it pushes the problem to a space where it does not have to be solved. If we start from the assumption of no bad students then we have to collect actual evidence to the contrary that survives analysis and peer review to locate where the help needs to be given. And this is very much my focus – support and help to bring people back to a positive educational experience. It’s too easy to assume things are false when it makes the job easier – as well absent a very human response for an over-worked sector. I think it’s time to plant some flags of assumed truths to change the way we talk and think about these things.
5 Things: Stuff I’ve Learned But Recently Had (Re)Confirmed
Posted: December 1, 2014 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, data visualisation, design, education, ethics, James Watson, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, thinking, tools 1 CommentOne of the advantages of getting older is that you realise that wisdom is merely the accumulated memory of the mistakes you made that haven’t killed you yet. Our ability to communicate these lessons as knowledge to other people determines how well we can share that wisdom around but, in many cases, it won’t ring true until someone goes through similar experiences. Here are five things that I’ve recently thought about because I have had a few decades to learn about the area and then current events have brought them to the fore. You may disagree with these but, as you will read in point 4, I encourage you to write your own rather than simply disagree with me.
- Racism and sexism are scientifically unfounded and just plain dumb. We know better.
I see that James Watson is selling his Nobel prize medal because he’d like to make some donations – oh, and buy some art. Watson was, rightly, shunned for expressing his belief that African-American people were less intelligent because they were… African-American. To even start from the incredibly shaky ground of IQ measurement is one thing but to then throw a healthy dollop of anti-African sentiment on top is pretty stupid. Read the second article to see that he’s not apologetic about his statements, he just notes that “you’re not supposed to say that”. Well, given that it’s utter rubbish, no, you should probably shouldn’t say it because it’s wrong, stupid and discriminatory. Our existing biases, cultural factors and lack of equal access to opportunity are facts that disproportionately affect African-Americans and women, to mention only two of the groups that get regularly hammered over this, but to think that this indicates some sort of characteristic of the victim is biassed privileged reasoning at its finest. Read more here. Read The Mismeasure of Man. Read recent studies that are peer-reviewed in journals by actual scientists.In short, don’t buy his medal. Give donations directly to the institutions he talks about if you feel strongly. You probably don’t want to reward an unrepentant racist and sexist man with a Hockney.
- Being aware of your privilege doesn’t make it go away.
I am a well-educated white man from a background of affluent people with tertiary qualifications. I am also married to a woman. My wife and I work full-time and have long-term employment with good salaries and benefits, living in a safe country that still has a reasonable social contract. This means that I have the most enormous invisible backpack of privilege, resilience and resources, to draw upon that means that I am rarely in any form of long-term distress at all. Nobody is scared when I walk into a room unless I pick up a karaoke microphone. I will be the last person to be discriminated against. Knowing this does not then make it ok if I then proceed to use my privilege in the world as if this is some sort of natural way of things. People are discriminated against every day. Assaulted. Raped. Tortured. Killed. Because they lack my skin colour, my gender, my perceived sexuality or my resources. They have obstacles in their path to achieving a fraction of my success that I can barely imagine. Given how much agency I have, I can’t be aware of my privilege without acting to grant as much opportunity and agency as I can to other people.As it happens, I am lucky enough to have a job where I can work to improve access to education, to develop the potential of students, to support new and exciting developments that might lead to serious and positive social change in the future. It’s not enough for me to say “Oh, yes, I have some privilege but I know about it now. Right. Moving on.” I don’t feel guilty about my innate characteristics (because it wasn’t actually my choice that I was born with XY chromosomes) but I do feel guilty if I don’t recognise that my continued use of my privilege generally comes at the expense of other people. So, in my own way and within my own limitations, I try to address this to reduce the gap between the haves and the have-nots. I don’t always succeed. I know that there are people who are much better at it. But I do try because, now that I know, I have to try to act to change things.
- Real problems take decades to fix. Start now.
I’ve managed to make some solid change along the way but, in most cases, these changes have taken 2-3 years to achieve and some of them are going to be underway for generations. One of my students asked me how I would know if we’d made a solid change to education and I answered “Well, I hope to see things in place by the time I’m 50 (four years from now) and then it will take about 25 years to see how it has all worked. When I retire, at 75, I will have a fairly good idea.”This is totally at odds with election cycles for almost every political sphere that work in 3-4 years, where 6-12 months is spent blaming the previous government, 24 months is spent doing something and the final year is spent getting elected again. Some issues are too big to be handled within the attention span of a politician. I would love to see things like public health and education become bipartisan issues with community representation as a rolling component of existing government. Keeping people healthy and educated should be statements everyone can agree on and, given how long it has taken me to achieve small change, I can’t see how we’re going to get real and meaningful improvement unless we start recognising that some things take longer than 2 years to achieve.
- Everyone’s a critic, fewer are creators. Everyone could be creating.
I love the idea of the manifesto, the public declaration of your issues and views, often with your aims. It is a way that someone (or a part of some sort) can say “these are the things that we care about and this is how we will fix the world”. There’s a lot inside traditional research that falls into this bucket: the world is broken and this is how my science will fix it! The problem is that it’s harder to make a definitive statement of your own views than it is to pick holes in someone else’s. As a logorrheic blogger, I have had my fair share of criticism over time and, while much of it is in the line of valuable discourse, I sometimes wonder if the people commenting would find it more useful to clearly define everything that they believe and then put it up for all to see.There is no doubt that this is challenging (my own educational manifesto is taking ages to come together as I agonise over semantics) but establishing what you believe to be important and putting it out there is a strong statement that makes you, as the author, a creator and it helps to find people who can assist you with your aims. By only responding to someone else’s manifesto, you are restricted to their colour palette and it may not contain the shades that you need.
Knowing what you believe is powerful, especially when you clearly identify it to yourself. Don’t wait for someone else to say something you agree with so that you can press the “Like” button or argue it out in the comments. Seize the keyboard!
- Money is stupid.
If you hadn’t picked up from point 2 how far away I am from the struggle of most of the 7 billion people on this planet, then this will bang that particular nail in. The true luxury of the privileged is to look at the monetary systems that control everyone else and consider other things because they can see what life in a non-scarcity environment is like. Everyone else is too busy working to have the time or headspace to see that we make money in order to spend money in order to make money because money. There’s roughly one accountant for every 250 people in the US and this is projected to rise by 13% to 2022 at exactly the same growth rate as the economy because you can’t have money without accounting for it, entering the paperwork, tracking it and so on. In the top 25 companies in the world, we see technology companies like Apple and Microsoft, resources companies like Exxon, PetroChina and BHP Biliton, giant consumer brands like Nestlé and Procter and Gamble … and investment companies and banks. Roughly 20% of the most valuable companies in the world exist because they handle vast quantities of money – they do not produce anything else. Capitalism is the ultimate Ponzi scheme.If you’ve read much of my stuff before then you know that a carrot-and-stick approach doesn’t help you to think. Money is both carrot and stick and, surprise, surprise, it can affect mechanical and simplistic performance but it can’t drive creativity or innovation. (It can be used to build an environment to support innovation but that’s another matter.) Weird, reality distorting things happen when money comes into play. People take jobs that they really don’t want to do because it pays better than something that they are good at or love. People do terrible things to other people to make more money and then, because they’re not happier, spend even more money and wonder what’s wrong. When we associate value and marks with things that we might otherwise love, bad things often happen as we can see (humorously) in Alexei Sayle’s Marxist demolition of Strictly Come Dancing.
Money is currently at the centre of our universe and it affects our thinking detrimentally, much as working with an Earth-centred model of the solar system doesn’t really work unless you keep making weird exceptions and complications in your models of reality. There are other models which, contrary to the fear mongering of the wealthy, does not mean that everyone has to live in squalor. In fact, if everyone were to live in squalor, we’d have to throw away a lot of existing resources because we already have about three billion people already living below $2.50 a day and we certainly have the resources to do better than that. Every second child in the world is living in poverty. Don’t forget that this means that the person who was going to cure cancer, develop starship travel, write the world’s greatest novel or develop working fusion/ultra-high efficiency solar may already have been born into poverty and may be one of the 22,000 children a day to die because of poverty.
We know this and we can see that this will require long-term, altruistic and smart thinking to fix. Money, however, appears to make us short-sighted, greedy and stupid. Ergo, money is stupid. Sadly, it’s an entrenched and currently necessary stupidity but we can, perhaps, hope for something better in the future.