A Break in the Silence: Time to Tell a Story
Posted: December 30, 2013 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, design, education, feedback, games, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, resources, storytelling, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, work/life balance, workload 2 CommentsIt has been a while since I last posted here but that is a natural outcome of focusing my efforts elsewhere – at some stage I had to work out what I had time to do and do it. I always tell my students to cut down to what they need to do and, once I realised that the time I was spending on the blog was having one of the most significant impacts on my ability to juggle everything else, I had to eat my own dogfood and cut back on the blog.
Of course, I didn’t do it correctly because instead of cutting back, I completely cut it out. Not quite what I intended but here’s another really useful piece of information: if you decide to change something then clearly work out how you are going to change things to achieve your goal. Which means, ahem, working out what your goals are first.
I’ve done a lot of interesting stuff over the last 6 months, and there are more to come, which means that I do have things to write about but I shall try and write about one a week as a minimum, rather than one per day. This is a pace that I hope to keep up and one that will mean that more of you will read more of what I write, rather than dreading the daily kiloword delivery.
I’ll briefly reflect here on some interesting work and seminars I’ve been looking at on business storytelling – taking a personal story, something authentic, and using it to emphasise a change in business behaviour or to emphasise a characteristic. I recently attended one of the (now defunct) One Thousand and One’s short seminars on engaging people with storytelling. (I’m reading their book “Hooked” at the moment. It’s quite interesting and refers to other interesting concepts as well.) I realise that such ideas, along with many of my notions of design paired with content, will have a number of readers peering at the screen and preparing a retort along the lines of “Storytelling? STORYTELLING??? Whatever happened to facts?”
Why storytelling? Because bald facts sometimes just don’t work. Without context, without a way to integrate information into existing knowledge and, more importantly, without some sort of established informational relationship, many people will ignore facts unless we do more work than just present them.
How many examples do you want: Climate Change, Vaccination, 9/11. All of these have heavily weighted bodies of scientific evidence that states what the answer should be, and yet there is powerful and persistent opposition based, largely, on myth and storytelling.
Education has moved beyond the rationing out of approved knowledge from the knowledge rich to those who have less. The tyrannical informational asymmetry of the single text book, doled out in dribs and drabs through recitation and slow scrawling at the front of the classroom, looks faintly ludicrous when anyone can download most of the resources immediately. And yet, as always, owning the book doesn’t necessarily teach you anything and it is the educator’s role as contextualiser, framer, deliverer, sounding board and value enhancer that survives the death of the drip-feed and the opening of the flood gates of knowledge. To think that storytelling is the delivery of fairytales, and that is all it can be, is to sell such a useful technique short.
To use storytelling educationally, however, we need to be focused on being more than just entertaining or engaging. Borrowing heavily from “Hooked”, we need to have a purpose in telling the story, it needs to be supported by data and it needs to be authentic. In my case, I have often shared stories of my time in working with computer networks, in short bursts, to emphasise why certain parts of computer networking are interesting or essential (purpose), I provide enough information to show this is generally the case (data) and because I’m talking about my own experiences, they ring true (authenticity).
If facts alone could sway humanity, we would have adopted Dewey’s ideas in the 1930s, instead of rediscovering the same truths decade after decade. If only the unembellished truth mattered, then our legal system would look very, very different. Our students are surrounded by talented storytellers and, where appropriate, I think those ranks should include us.
Now, I have to keep to the commitment I made 8 months ago, that I would never turn down the chance to have one of my cats on my lap when they wanted to jump up, and I wish you a very happy new year if I don’t post beforehand.
Skill Games versus Money Games: Disguising One Game As Another
Posted: July 5, 2013 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, blogging, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, feedback, games, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, plagiarism, principles of design, reflection, resources, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design Leave a commentI recently ran across a very interesting article on Gamasutra on the top tips for turning a Free To Play (F2P) game into a Paying game by taking advantage of the way that humans think and act. F2P games are quite common but, obviously, it costs money to make a game so there has to be some sort of associated revenue stream. In some cases, the F2P is a Lite version of the pay version, so after being hooked you go and buy the real thing. Sometimes there is an associated advertising stream, where you viewing the ads earns the producer enough money to cover costs. However, these simple approaches pale into insignificance when compared with the top tips in the link.
Ramin identifies two games for this discussion: games of skill, where it is your ability to make sound decisions that determines the outcome, and money games, where your success is determined by the amount of money you can spend. Games of chance aren’t covered here but, given that we’re talking about motivation and agency, we’re depending upon one specific blindspot (the inability of humans to deal sensibly with probability) rather than the range of issues identified in the article.
I dont want to rehash the entire article but the key points that I want to discuss are the notion of manipulating difficulty and fun pain. A game of skill is effectively fun until it becomes too hard. If you want people to keep playing then you have to juggle the difficulty enough to make it challenging but not so hard that you stop playing. Even where you pay for a game up front, a single payment to play, you still want to get enough value out of it – too easy and you finish too quickly and feel that you’ve wasted your money; too hard and you give up in disgust, again convinced that you’ve wasted your money. Ultimately, in a pure game of skill, difficulty manipulation must be carefully considered. As the difficulty ramps up, the player is made uncomfortable, the delightful term fun pain is applied here, and resolving the difficulty removes this.
Or, you can just pay to make the problem go away. Suddenly your game of skill has two possible modes of resolution: play through increasing difficulty, at some level of discomfort or personal inconvenience, or, when things get hard enough, pump in a deceptively small amount of money to remove the obstacle. The secret of the P2P game that becomes successfully monetised is that it was always about the money in the first place and the initial rounds of the game were just enough to get you engaged to a point where you now have to pay in order to go further.
You can probably see where I’m going with this. While it would be trite to describe education as a game of skill, it is most definitely the most apt of the different games on offer. Progress in your studies should be a reflection of invested time in study, application and the time spent in developing ideas: not based on being ‘lucky’, so the random game isn’t a choice. The entire notion of public education is founded on the principle that educational opportunities are open to all. So why do some parts of this ‘game’ feel like we’ve snuck in some covert monetisation?
I’m not talking about fees, here, because that’s holding the place of the fee you pay to buy a game in the first place. You all pay the same fee and you then get the same opportunities – in theory, what comes out is based on what the student then puts in as the only variable.
But what about textbooks? Unless the fee we charge automatically, and unavoidably, includes the cost of the textbook, we have now broken the game into two pieces: the entry fee and an ‘upgrade’. What about photocopying costs? Field trips? A laptop computer? An iPad? Home internet? Bus fare?
It would be disingenuous to place all of this at the feet of public education – it’s not actually the fault of Universities that financial disparity exists in the world. It is, however, food for thought about those things that we could put into our courses that are useful to our students and provide a paid alternative to allow improvement and progress in our courses. If someone with the textbook is better off than someone without the textbook, because we don’t provide a valid free alternative, then we have provided two-tiered difficulty. This is not the fun pain of playing a game, we are now talking about genuine student stress, a two-speed system and a very high risk that stressed students will disengage and leave.
From my earlier discussions on plagiarism, we can easily tie in Ramin’s notion of the driver of reward removal, where players have made so much progress that, on facing defeat, they will pay a fee to reduce the impact of failure; or, in some cases, to remove it completely. As Ramin notes:
“This technique alone is effective enough to make consumers of any developmental level spend.”
It’s not just lost time people are trying to get back, it’s the things that have been achieved in that time. Combine that with, in our case, the future employability and perception of that piece of paper, and we have a very strong behavioural driver. A number of the tricks Ramin describes don’t work as well on mature and aware thinkers but this one is pretty reliable. If it’s enough to make people pay money, regardless of their development level, then there are lots of good design decisions we can make from this – lower risk assessment, more checkpointing, steady progress towards achievement. We know lots of good ways to avoid this, if we consider it to be a problem and want to take the time to design around it.
This is one of the greatest lessons I’ve learned about studying behaviour, even as a rank amateur. Observing what people do and trying to build systems that will work despite that makes a lot more sense than building a system that works to some ideal and trying to jam people into it. The linked article shows us how people are making really big piles of money by knowing how people work. It’s worth looking at to make sure that we aren’t, accidentally, manipulating students in the same way.
The defining question.
Posted: July 2, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, community, education, educational problem, ethics, feedback, higher education, in the student's head, reflection, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, workload Leave a commentThere has been a lot going on for me recently. A lot of thinking, a lot of work and an amount of getting involved in things because my students trust me and will come to me to ask questions, which sometimes puts me in the uncomfortable position of having to juggle my accommodation for the different approaches of my colleagues and my own beliefs, as well as acting in everyone’s best interests. I’m not going to go into details but I think that I can summarise my position on everything, as an educator, by phrasing it in one question.
Is this course of action to the student’s benefit?
I mean, that’s it, isn’t it? If the job is educating students and developing the citizens of tomorrow, then everything that we do should be to the benefit of the student and/or future graduate. But it’s never simple, is it, because the utilitarian calculus to derive benefit quickly becomes complicated when we consider the effect of institutional reputation or perception on the future benefit to the student. But maybe that’s over thinking things (gasp, I hear regular readers cry). I’m not sure I know how to guide student behaviour to raise my University’s ranking in various measures – but I do know how to guide student behaviour to reduce the number of silly or thoughtless things they do, to enhance their learning and to help them engage. Maybe the simple question is the best? Will the actions I take today improve my students’ knowledge or enhance their capacity to learn? Have I avoided wasting their time doing something that we do because we have always done it, rather than giving them something to do because it is what we should be doing? Am I always considering the benefit to the largest group of students, while considering the needs of the individual?
Every time I see a system that has a fixed measure of success, people optimise for it. If it’s maximum profit, people maximise profit. If it’s minimum space, people cut their space. Guidelines help a lot in working out which course of action to take: when faced with a choice between A and B, choose the option that maximises your objective. This even works without a strong vision of the future, which is good because I’m not sure we have a clear enough view of the long path to graduation to really be specific about this. There is always a risk that people will get the assessment of benefit wrong, which can lead to soft marking or lax standards, but I’m not a believer that post hoc harshness is the solution to inherited laxity from another system (especially where that may be a perception that’s not grounded in reality). Looking at all of my actions in terms of a real benefit, to the student, to their community, to our equality standards, to our society – that shines a bright light on what we do so we can clearly see what we’re doing and, if it requires change, illuminates the path to change.
Another semester, more lessons learned (mostly by me).
Posted: June 16, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, collaboration, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, plagiarism, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design Leave a commentI’ve just finished the lecturing component for my first year course on programming, algorithms and data structures. As always, the learning has been mutual. I’ve got some longer posts to write on this at some time in the future but the biggest change for this year was dropping the written examination component down and bringing in supervised practical examinations in programming and code reading. This has given us some interesting results that we look forward to going through, once all of the exams are done and the marks are locked down sometime in late July.
Whenever I put in practical examinations, we encounter the strange phenomenon of students who can mysteriously write code in very short periods of time in a practical situation very similar to the practical examination, but suddenly lose the ability to write good code when they are isolated from the Internet, e-Mail and other people’s code repositories. This is, thank goodness, not a large group (seriously, it’s shrinking the more I put prac exams in) but it does illustrate why we do it. If someone has a genuine problem with exam pressure, and it does occur, then of course we set things up so that they have more time and a different environment, as we support all of our students with special circumstances. But to be fair to everyone, and because this can be confronting, we pitch the problems at a level where early achievement is possible and they are also usually simpler versions of the types of programs that have already been set as assignment work. I’m not trying to trip people up, here, I’m trying to develop the understanding that it’s not the marks for their programming assignments that are important, it’s the development of the skills.
I need those people who have not done their own work to realise that it probably didn’t lead to a good level of understanding or the ability to apply the skill as you would in the workforce. However, I need to do so in a way that isn’t unfair, so there’s a lot of careful learning design that goes in, even to the selection of how much each component is worth. The reminder that you should be doing your own work is not high stakes – 5-10% of the final mark at most – and builds up to a larger practical examination component, worth 30%, that comes after a total of nine practical programming assignments and a previous prac exam. This year, I’m happy with the marks design because it takes fairly consistent failure to drop a student to the point where they are no longer eligible for redemption through additional work. The scope for achievement is across knowledge of course materials (on-line quizzes, in-class scratchy card quizzes and the written exam), programming with reference materials (programming assignments over 12 weeks), programming under more restricted conditions (the prac exams) and even group formation and open problem handling (with a team-based report on the use of queues in the real world). To pass, a student needs to do enough in all of these. To excel, they have to have a good broad grasp of theoretical and practical. This is what I’ve been heading towards for this first-year course, a course that I am confident turns out students who are programmers and have enough knowledge of core computer science. Yes, students can (and will) fail – but only if they really don’t do enough in more than one of the target areas and then don’t focus on that to improve their results. I will fail anyone who doesn’t meet the standard but I have no wish to do any more of that than I need to. If people can come up to standard in the time and resource constraints we have, then they should pass. The trick is holding the standard at the right level while you bring up the people – and that takes a lot of help from my colleagues, my mentors and from me constantly learning from my students and being open to changing the learning design until we get it right.
Of course, there is always room for improvement, which means that the course goes back up on blocks while I analyse it. Again. Is this the best way to teach this course? Well, of course, what we will do now is to look at results across the course. We’ll track Prac Exam performance across all practicals, across the two different types of quizzes, across the reports and across the final written exam. We’ll go back into detail on the written answers to the code reading question to see if there’s a match for articulation and comprehension. We’ll assess the quality of response to the exam, as well as the final marked outcome, to tie this back to developmental level, if possible. We’ll look at previous results, entry points, pre-University marks…
And then we’ll teach it again!
The Continuum of Ethical Challenge: Why the Devil Isn’t Waiting in the Alleyway and The World is Harder than Bioshock.
Posted: June 15, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, community, curriculum, design, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, principles of design, reflection, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking Leave a commentThis must be a record for a post title but I hope to keep the post itself shortish. Years ago, when I was still at school, a life counsellor (who was also a pastor) came to talk to us about life choices and ethics. He was talking about the usual teen cocktail: sex, drugs and rebellion.. However, he made an impression on me by talking about his early idea of temptation. Because of the fire and brimstone preaching he’d grown up with, he half expected temptation to take the form of the Devil, beckoning him into an alleyway to take an illicit drag on a cigarette. As he grew up, and grew wiser, he realised that living ethically was really a constant set of choices, interlocking or somewhat dependant, rather than an easy life periodically interrupted by strictly defined challenges that could be overcome with a quick burst of willpower.
I recently started replaying the game Bioshock, which I have previously criticised elsewhere, and was struck by the facile nature of the much-vaunted ethical aspect to game play. For those who haven’t played it, you basically have a choice between slaughtering or saving little girls – apart from that, you have very little agency or ability to change the path you’re on. In fact, rather than provide you with the continual dilemma of whether you should observe, ignore or attack the inhabitants of the game world, you very quickly realise that there are no ‘good’ people in the world (or there are none that you are actually allowed to attack, they are all carefully shielded from you) so you can reduce your ‘choices’ when encountering a figure crouching over a pram to “should I bludgeon her to death, or set her on fire and shoot her in the head”. (It’s ok, if you try anything approaching engagement, she will try and kill you.) In fact, one of the few ‘innocents’ in the game is slaughtered in front of you while you watch impotently. So your ethical engagement is restricted, at very distinctly defined intervals, to either harvesting or rescuing the little girls who have been stolen from orphanages and turned into corpse scavenging monsters. This is as ridiculous as the intermittent Devil in the alleyway, in fact, probably more so!
I completely agree with that counsellor from (goodness) 30 years ago – it would be a nonsense to assume that tests of our ethics can be conveniently compartmentalised to a time when our resolve is strong and can be so easily predicted. The Bioshock model (or models like it, such as Call of Duty 4, where everyone is an enemy or can’t be shot in a way that affects our game beyond a waggled finger and being taken back to a previous save) is flawed because of the limited extent of the impact of the choices you make – in fact, Bioshock is particularly egregious because the ‘outcome’ of your moral choice has no serious game impact except to show you a different movie at the end. Before anyone says “it’s only a game”, I agree, but they were the ones who imposed the notion that this ethical choice made a difference. Games such as Deus Ex gave you very much un-cued opportunities to intervene or not – with changes to the game world depending on what happened. As a result, people playing Deus Ex had far more moral engagement with the game and everyone I’ve spoken to felt as if they were making the choices that led to the outcome: autonomy, mastery and purpose anyone? That was in 2000 – very few games actually see the world as one that you can influence (although some games are now coming up to par on this).
I think about this a lot for my learning design. While my students may recognise ethical choices in the real world, I am always concerned that a learning design that reduces their activities to high stakes hurdle challenges will mimic the situation where we have, effectively, put the Devil in the alleyway and you can switch on your ‘ethical’ brain at this point. I posed a question to my students in their sample exam where I proposed that they had commissioned someone to write their software for an assignment – and them asked to think about the effect that this decision would have on their future self in terms of knowledge development, if we assumed that they would always be better prepared if they did the work themselves. This takes away the focus from the day or so leading up to an individual assignment and starts to encourage continuum thinking, where every action is take as part of a whole life of ethical actions. I’m a great believer that skills only develop with practice and knowledge only stays in your head when you reinforce it, so any opportunity to encourage further development of ethical thinking is to be encouraged!
“Hi, my name is Nick and I specialise in failure.”
Posted: June 10, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, collaboration, community, curriculum, design, education, educational research, ethics, failure, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, reflection, resources, student perspective, survivorship, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools Leave a commentI recently read an article on survivorship bias in the “You Are Not So Smart” website, via Metafilter. While the whole story addressed the World War II Statistical Research Group, it focused on the insight contributed by Abraham Wald, a statistician. The World War II Allied bomber losses were large, very large, and any chances of reducing this loss was incredibly valuable. The question was “How could the US improve their chances of bringing their bombers back intact?” Bombers landing back after missions were full of holes but armour just can’t be strapped willy-nilly on to a plane without it becoming land-locked. (There’s a reason that birds are so light!) The answer, initially, was obvious – find the place where the most holes were, by surveying the fleet, and patching them. Put armour on the colander sections and, voila, increased survival rate.
No, said Wald. That wouldn’t help.
Wald’s logic is both simple and convincing. If a plane was coming back with those holes in place, then the holes in the skin were not leading to catastrophic failure – they couldn’t have been if the planes were returning! The survivors were not showing the damage that would have led to them becoming lost aircraft. Wald used the already collected information on the damage patterns to work out how much damage could be taken on each component and the likelihood of this occurring during a bombing run. based on what kind of forces it encountered.
It’s worth reading the entire article because it’s a simple and powerful idea – attributing magical properties to the set of steps taken by people who have become ultra-successful is not going to be as useful as looking at what happened to take people out of the pathway to success. If you’ve read Steve Jobs’ biography then you’re aware that he had a number of interesting traits, only some of which may have led to him becoming as successful as he did. Of course, if you’ve been reading a lot, you’ll be aware of the importance of Paul Jobs, Steve Wozniak, Robert Noyce, Bill Gates, Jony Ive, John Lasseter, and, of course, his wife, Laurene Powell Jobs. So the whole “only eating fruit” thing, the “reality distortion field” thing and “not showering” thing (some of which he changed, some he didn’t) – which of these are the important things? Jobs, like many successful people, failed at some of his endeavours, but never in a way that completely wiped him out. Obviously. Now, when he’s not succeeding, he’s interesting, because we can look at the steps that took him down and say “Oh, don’t do that”, assuming that it’s something that can be changed or avoided . When he’s succeeding, there are so many other things getting in the way that depend upon what’s happened to you so far, who your friends are, and how many resources you get to play with, it’s hard to be able to give good advice on what to do.
I have been studying failure for some time. Firstly in myself, and now in my students. I look for those decisions, or behaviours, that lead to students struggling in their academic achievement, or to falling away completely in some cases. The majority of the students who come to me with a high level of cultural, financial and social resources are far less likely to struggle because, even when faced with a set-back, they rarely hit the point where they can’t bounce back – although, sadly, it does happen but in far fewer numbers. When they do fall over, it is for the same reasons as my less-advantaged students, who just do so in far greater numbers because they have less resilience to the set-backs. By studying failure, and the lessons learned and the things to be avoided, I can help all of my students and this does not depend upon their starting level. If I were studying the top 5% of students, especially those who had never received a mark less than A+, I would be surprised if I could learn much that I could take and usefully apply to those in the C- bracket. The reverse, however? There’s gold to be mined there.
By studying the borderlines and by looking for patterns in the swirling dust left by those departing, I hope that I can find things which reduce failure everywhere – because every time someone fails, we run the risk of not getting them back simply because failure is disheartening. Better yet, I hope to get something that is immediately usable, defensible and successful. Probably rather a big ask for a protracted study of failure!
Note to Self
Posted: May 19, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: authenticity, community, education, educational problem, ethics, higher education, in the student's head, learning, marcus aurelius, meditations, reflection, resources, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking 3 CommentsI’ve mentioned the “Meditations” of the Emperor Marcus Aurelius before – I’ve been writing this blog for over 450 hours, I’m not sure there’s anything I haven’t mentioned except my feelings on the season finale of Doctor Who, Series 7. (Eh.) Marcus Aurelius, philosopher, statesman, Roman, and Emperor wrote twelve “books” which were apparently never meant to be published. These are the private musings, notes to self, of a thoughtful man, written stoically and Stoically. When he lectures anyone, he lectures himself. He even poses questions to parts of himself: his soul, most notably.
There is much to admire in the simplicity and purpose of Marcus Aurelius’ thoughts. They are brief, because Emperors are busy people, especially when earning titles such as Germanicus (which usually involves squashing a nation state or two). They are direct, because he is talking to himself and he needs to be honest. He repeats himself for emphasis and to indicate importance, not out of forgetfulness.
Best, he writes for himself, for clarity, for the now and without thinking of a future audience.
There is a great deal to think about in this, because if you have read “Meditations”, you will know that every page contains a gem and some pages have jewels cascading from them. Yet these are the private thoughts of a person recording ways to improve himself and to keep himself in check – while he managed the Roman empire.
When I talk about improvement, I’m always trying to improve myself. When I find fault, I’ve usually found it in myself first. Yet, what a lot of words I write! Perhaps it is time to reinvestigate brevity, directness and a generosity towards the self that translates well into a kindness to strangers who might stumble upon this. The last thing I’d want to do is to stop people finding what zircons there are because the preamble is too demanding or the journey to the point too long.
Once again, I give my thanks to the writings of someone who died 2000 years ago and gave me so much to think about. Vale, Marcus Aurelius.
Time to Work and Time to Play
Posted: May 19, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, education, educational problem, educational research, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, work/life balance, workload 1 CommentI do a lot of grounded theory research into student behaviour patterns. It’s a bit Indiana Jones in a rather dry way: hear a rumour of a giant cache of data, hack your way through impenetrable obfuscation and poor data alignment to find the jewel at the centre, hack your way out and try to get it to the community before you get killed by snakes, thrown into a propellor or eaten. (Perhaps the analogy isn’t perfect but how recently have you been through a research quality exercise?) Our students are all pretty similar, from the metrics I have, and I’ve gone on at length about this in other posts: hyperbolic time-discounting and so on. Embarrassingly recently, however, I was introduced to the notion of instrumentality, the capability to see that achieving a task now will reduce the difficulty in completing a goal later. If we can’t see how important this is to getting students to do something, maybe it’s time to have a good sit-down and a think! Husman et al identify three associated but distinguishable aspects to a student’s appreciation of a task: how much they rate its value, their intrinsic level of motivation, and their appreciation of the instrumentality. From this study, we have a basis for the confusing and often paradoxical presentation of a student who is intelligent and highly motivated – but just not for the task we’ve given them, despite apparently and genuinely being aware of the value of the task. Without the ability to link this task to future goal success, the exponential approach of the deadline horizon can cause a student to artificially inflate the value of something of less final worth, because the actual important goal is out of sight. But rob a student of motivation and we have to put everything into a high-stakes, heavily temporally fixed into the almost immediate future and the present, often resorting to extrinsic motivating factors (bribes/threats) to impose value. This may be why everyone who uses a punishment/reward situation achieves compliance but then has to keep using this mechanism to continue to keep values artificially high. Have we stumbled across an Economy of Pedagogy? I hope not, because I can barely understand basic economics. But we can start to illustrate why the student has to be intrinsically connected to the task and the goal framework – without it, it’s carrot/stick time and, once we do that, it’s always carrot/stick time.
Like almost every teacher I know, all of my students are experts at something but mining that can be tricky. What quickly becomes apparent, and as McGonigall reflected on in “Reality is Broken”, is that people will put far more effort into an activity that they see as play than one which they see as work. I, for example, have taken up linocut printing and, for no good reason at all, have invested days into a painstaking activity where it can take four hours to achieve even a simple outcome of reasonable quality – and it will be years before I’m good at it. Yet the time I spend at the printing studio on Saturdays is joyful, recharging and, above all, playful. If I consumed 6 hours marking assignments, writing a single number out of 10 and restricting my comments to good/bad/try harder, then I would feel spent and I would dread starting, putting it off as long as possible. Making prints, I consumed about 6 hours of effort to scan, photoshop, trim, print, reverse, apply over carbon paper, trace, cut out of lino and then manually and press print about four pieces of paper – and I felt like a new man. No real surprises here. In both cases, I am highly motivated. One task has great value to my students and me because it provides useful feedback. The artistic task has value to me because I am exploring new forms of art and artistic thinking, which I find rewarding.
But what of the instrumentality? In the case of the marking, it has to be done at a time where students can get the feedback at a time where they can use it and, given we have a follow-up activity of the same type for more marks, they need to get that sooner rather than later. If I leave it all until the end of the semester, it makes my students’ lives harder and mine, too, because I can’t do everything at once and every single ‘when is it coming’ query consumes more time. In the case of the art, I have no deadline but I do have a goal – a triptych work to put on the wall in August. Every print I make makes this final production easier. The production of the lino master? Intricate, close work using sharp objects and it can take hours to get a good result. It should be dull and repetitive but it’s not – but ask me to cut out 10 of the same thing or very, very similar things and I think it would be, very quickly. So, even something that I really enjoy becomes mundane when we mess with the task enough or get to the point, in this case, where we start to say “Well, why can’t a machine do this?” Rephrasing this, we get the instrumentality focus back again: “What do I gain in the future from doing this ten times if I will only do this ten times once?” And this is a valid question for our students, too. Why should they write “Hello, World” – it has most definitely and definitively been written. It’s passed on. It is novel no more. Bereft of novelty, it rests on its laurels. If we didn’t force students to write it, there is no way that this particular phrase, which we ‘owe’ to Brian Kernighan, is introducing anyone to anything that could not have a modicum of creativity added to it by saying in the manual “Please type a sentence into this point in the program and it will display it back to you.” It is an ex-program.
I love lecturing. I love giving tutorials. I will happily provide feedback in pracs. Why don’t I like marking? It’s easy to say “Well, it’s dull and repetitive” but, if I wouldn’t ask a student to undertake a task like that so why am I doing it? Look, I’m not advocating that all marking is like this but, certainly, the manual marking of particular aspects of software does tend to be dull.
Unless, of course, you start enjoying it and we can do that if we have enough freedom and flexibility to explore playful aspects. When I marked a big group of student assignments recently, I tried to write something new for each student and, this doesn’t always succeed for small artefacts with limited variability, I did manage to complement a student on their spanish variable names, provide personalised feedback to some students who had excelled and, generally, turned a 10 mark program into a place where I thought about each student personally and then (more often than not) said something unique. Yes, sometimes the same errors cropped up and the copy/paste is handy – but by engaging with the task and thinking about how much my future interactions with the students would be helped with a little investment now, the task was still a slog, but I came out of it quite pleased with the overall achievement. The task became more enjoyable because I had more flexibility but I also was required to be there to be part of the process, I was necessary. It became possible to be (professionally and carefully) playful – which is often how I approach teaching.
Any of you who are required to use standardised tests with manual marking: you already know how desperately dull the grading is and it is a grindingly dull, rubric-bound, tick/flick scenario that does nothing except consume work. It’s valuable because it’s required and money is money. Motivating? No. Any instrumentality? No, unless giving the test raises the students to the point where you get improved circumstances (personal/school) or you reduce the amount of testing required for some reason. It is, sadly, as dull for your students to undertake them, in this scenario, because they will know how it’s marked and it is not going to trigger any of Husman’s three distinguished but associated variables.
I am never saying that everything has to fun or easy, because I doubt many areas would be able to convey enough knowledge under these strictures, but providing tasks that have room to encourage motivation, develop a personal sense of task value, and that allow students to play, potentially bringing in some of their own natural enthusiasm on other areas or channeling it here, solves two thirds of the problem in getting students involved. Intentionally grounding learning in play and carefully designing materials to make this work can make things better. It also makes it easier for staff. Right now, as we handle the assignment work of the course I’m currently teaching, other discussions on the student forums includes the History of Computing, Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions, the significance of certain questions in the practical, complexity theory and we have only just stopped the spontaneous student comparison of performance at a simple genetic algorithms practical. My students are exploring, they are playing in the space of the discipline and, by doing so, are moving more deeply into a knowledge of taxonomy and lexicon within this space. I am moving from Lion Tamer to Ringmaster, which is the logical step to take as what I want is citizens who are participating because they can see value, have some level of motivation and are forming their instrumentality. If learning and exploration is fun now, then going further in this may lead to fun later – the future fun goal is enhanced by achieving tasks now. I’m not sure if this is necessarily the correct first demonstration of instrumentality, but it is a useful one!
However, it requires time for both the staff member to be able to construct and moderate such an environment, especially if you’re encouraging playful exploration of areas on public discussion forums, and the student must have enough time to be able to think about things, make plans and then to try again if they don’t pick it all up on the first go. Under strict and tight deadlines, we know the creativity can be impaired when we enforce the deadlines the wrong way, and we reduce the possibility of time for exploration and play – for students and staff.
Playing is serious business and our lives are better when we do more of it – the first enabling act of good play is scheduling that first play date and seeing how it goes. I’ve certainly found it to be helpful, to me and to my students.
The Kids are Alright (within statistical error)
Posted: April 21, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: blogging, community, data visualisation, design, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, reflection, thinking, tools 3 CommentsYou may have seen this quote, often (apparently inaccurately) attributed to Socrates:
“The children now love luxury; they have bad manners, contempt for authority; they show disrespect for elders and love chatter in place of exercise. Children are now tyrants, not the servants of their households. They no longer rise when elders enter the room. They contradict their parents, chatter before company, gobble up dainties at the table, cross their legs, and tyrannize their teachers.” (roughly 400BC)
Apparently this is either a paraphrase of Aristophanes or misquoted Plato – like all things attributed to Socrates, we have to remember that we don’t have his signature to any of them. However, it doesn’t really matter if Socrates said it because not only did Hesiod say something in 700BC:
“I see no hope for the future of our people if they are dependent on frivolous youth of today, for certainly all youth are reckless beyond words… When I was young, we were taught to be discreet and respectful of elders, but the present youth are exceedingly wise [disrespectful] and impatient of restraint”
And then we have Peter the Hermit in 1274AD:
“The world is passing through troublous times. The young people of today think of nothing but themselves. They have no reverence for parents or old age. They are impatient of all restraint. They talk as if they knew everything, and what passes for wisdom with us is foolishness with them. As for the girls, they are forward, immodest and unladylike in speech, behavior and dress.”
(References via the Wikiquote page of Socrates and a linked discussion page.)
Let me summarise all of this for you:
You dang kids! Get off my lawn.
As you know, I’m a facty-analysis kind of guy so I thought that, if these wise people were correct and every generation is steadily heading towards mental incapacity and moral turpitude, we should be able to model this. (As an aside, I love the word turpitude, it sounds like the state of mind a turtle reaches after drinking mineral spirits.)
So let’s do this, let’s assume that all of these people are right and that the youth are reckless, disrespectful and that this keeps happening. How do we model this?
It’s pretty obvious that the speakers in question are happy to set themselves up as people who are right, so let’s assume that a human being’s moral worth starts at 100% and that all of these people are lucky enough to hold this state. Now, since Hesiod is chronologically the first speaker, let’s assume that he is lucky enough to be actually at 100%. Now, if the kids aren’t alright, then every child born will move us away from this state. If some kids are ok, then they won’t change things. Of course, every so often we must get a good one (or Socrates’ mouthpiece and Peter the Hermit must be aliens) so there should be a case for positive improvement. But we can’t have a human who is better than 100%, work with me here, and we shall assume that at 0% we have the worst person you can think of.
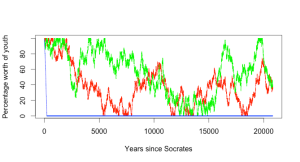
What we are now modelling is a random walk, starting at 100 and then adding some combination of -1, 0 or 1 at some regular interval. Let me cut to the chase and show you what this looks like, when modelled. I’ve assumed, for ease of modelling, that we make the assessment of the children every year and we have at most a 1 percentile point shift in that year, whatever other assumptions I made. I’ve provided three different models, one where the kids are terrible – we choose very year from no change or a negative shift. The next model is that the kids have some hope but sometimes do nothing, and we choose from an improvement, no change or steady moral decline! The final model is one where we either go up or down. Let’s look at a random walk across all three models over the span of years from 700BC to today:
As you can see, if we take the dire predictions of the next generation as true, then it is only a few hundred years before everything collapses. However, as expected, random walks over this range move around and hit a range of values. (Right now, you should look up Gambler’s Ruin to see why random walks are interesting – basically, over an infinite time, you’d expect to hit all of the values in the range from 0 to 100 an infinite number of times. This is why gamblers with small pots of money struggle against casinos with effectively infinite resources. Maths.)
But we know that the ‘everything is terrible’ model doesn’t work because both Socrates and Peter the Hermit consider themselves to be moral and both lived after the likely ‘decline to zero’ point shown in the blue line. But what would happen over longer timeframes? Let’s look at 20,000 and 200,000 years respectively. (These are separately executed random walks so the patterns will be different in each graph.)
What should be apparent, even with this rather pedantic exploration of what was never supposed to be modelled is that, even if we give credence to these particular commentators and we accept that there is some actual change that is measurable and shows an improvement or decline between generations, the negative model doesn’t work. The longer we run this, the more it will look like the noise that it is – and that is assuming that these people were right in the first place.
Personally, I think that the kids of this generation are pretty much the same as the one before, with some different adaptation to technology and societal mores. Would I have wasted time in lectures Facebooking if I had the chance? Well, I wasted it doing everything else so, yes, probably. (Look around your next staff meeting to see how many people are checking their mail. This is a technological shift driven by capability, not a sign of accelerating attention deficit.) Would I have spent tons of times playing games? Would I? I did! They were just board, role-playing and simpler computer games. The kids are alright and you can see that from the graphs – within statistical error.
Every time someone tells me that things are different, but it’s because the students are not of the same calibre as the ones before… well, I look at these quotes over the past 2,500 and I wonder.
And I try to stay off their lawn.
Tell us we’re dreaming.
Posted: April 21, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, education, Generation Why, higher education, reflection, resources, thinking, work/life balance, workload 2 CommentsI recently read an opinion piece in the Australian national newspaper, the conveniently named “The Australian”, on funding school reform. The piece, entitled “School Reform must be funded” and sub-titled “But maybe we need fewer academics thinking up ways to spend our taxes”, written by Cassandra Wilkinson, identified that the coming cuts to higher education because of the apparent impossibility of paying for school reforms in any other way. No-one, sensible, is arguing that the school cuts can come out of thin air, I make explicit reference to realities such as this in my previous post, but it does appear that Cassandra is attempting to place the blame squarely on the shoulders of the academics, for this sorry state of affairs (“the growing influence of the university sector on early childhood and school education is partly responsible for the now necessary cuts to higher education.”, from the article).
It is the professionalisation of teaching, and the intervention of education academics to convince governments that early educational investment, potentially at the expense of the family unit’s role in child rearing, that has convinced governments that money must be spent here – therefore, it is our fault that our argument is leading to money coming out of our pockets. I cannot think of a more amazing piece of victim blaming, recently, but then again I generally don’t read the opinion section of The Australian!
Now, you may immediately say “You must be quoting her out of context”, here is another extract from this rather short opinion piece:
“In addition to the public costs being generated by education academics, we have public health academics driving an expensive “preventative health” agenda that includes mental health checks for kids and public advertising about the calorie content of pizza; safety academics driving up the cost of road building and tripling the price of trampolines, which now come with fencing and crash mats; and sustainability academics driving up the cost of housing.”
Not only are people concerned about education driving up the cost of education but we have increased all other prices through our short-sighted adherence to preventative health, safety and sustainability! I keep thinking that Wilkinson, who has some quiet excellent social project credentials if I have researched the correct Cassandra Wilkinson, must be making a satirical comment here but, either my humour is failing (entirely possible), she has been edited (entirely possible) or she is completely serious and we in higher education have brought doom upon our heads by dint of doing our job. The piece finishes with:
“It may well be that the real efficiency savings will derive from a university sector employing slightly fewer academics to dream up new ways for governments to spend taxpayers money.”
and whether this is intended to be satire or not, this statement does raise my hackles.
Right now, most of the academics I know are trying to dream up ways to meet our obligations to our students in terms of a high-quality, useful and valuable education under existing restrictions. The only tax spending we’re trying to do is on the things that we can barely afford to do on the monies we get. I’m assuming that Cassandra is being satirical but is just not very good at it – or is assuming the role of her namesake, in that no-one will actually take her seriously, which is a shame as the approach that she seems to be supporting is not just saying that the only place this money can come from is higher ed, but that we should shut up because of how much we’re costing decent, family-centered Australians. If only I had that many column inches in a large-scale distribution paper to put my case that, maybe, people should stop talking about what they think we’re doing, or their fuzzy memories of old Uni days and bad movies, and come down and see what we’re doing now. Shadow me for a month. Bring running shoes. But, hey, maybe I’m just lazy, soft and dreamy. How would I know?
The rich dream of luxuries, the poor dream of staples. We are dreaming of having enough to do our jobs adequately and these are not the dreams of rich people.
Maybe I’m just too tired right now to see her humour in all of this. I seriously hope that I’ve just got the wrong end of the stick, because if this is what the social progressives are saying, then we may as well close up shop now.