Think. Create. Code. Vis! (@edXOnline, @UniofAdelaide, @cserAdelaide, @code101x, #code101x)
Posted: April 30, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: #code101x, advocacy, blogging, collaboration, community, curriculum, data visualisation, education, educational problem, educational research, edx, higher education, learning, measurement, MOOC, moocs, reflection, resources, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design Leave a commentI just posted about the massive growth in our new on-line introductory programming course but let’s look at the numbers so we can work out what’s going on and, maybe, what led to that level of success. (Spoilers: central support from EdX helped a huge amount.) So let’s get to the data!
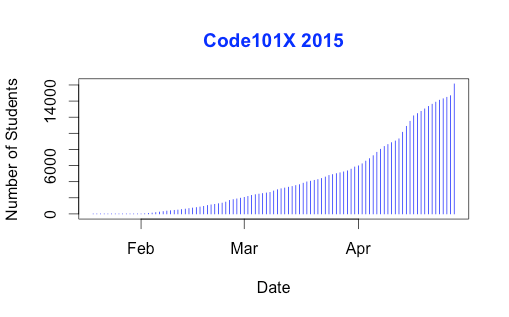
I love visualised data so let’s look at the growth in enrolments over time – this is really simple graphical stuff as we’re spending time getting ready for the course at the moment! We’ve had great support from the EdX team through mail-outs and Twitter and you can see these in the ‘jumps’ in the data that occurred at the beginning, halfway through April and again at the end. Or can you?
Hmm, this is a large number, so it’s not all that easy to see the detail at the end. Let’s zoom in and change the layout of the data over to steps so we can things more easily. (It’s worth noting that I’m using the free R statistical package to do all of this. I can change one line in my R program and regenerate all of my graphs and check my analysis. When you can program, you can really save time on things like this by using tools like R.)

Now you can see where that increase started and then the big jump around the time that e-mail advertising started, circled. That large spike at the end is around 1500 students, which means that we jumped 10% in a day.
When we started looking at this data, we wanted to get a feeling for how many students we might get. This is another common use of analysis – trying to work out what is going to happen based on what has already happened.
As a quick overview, we tried to predict the future based on three different assumptions:
- that the growth from day to day would be roughly the same, which is assuming linear growth.
- that the growth would increase more quickly, with the amount of increase doubling every day (this isn’t the same as the total number of students doubling every day).
- that the growth would increase even more quickly than that, although not as quickly as if the number of students were doubling every day.
If Assumption 1 was correct, then we would expect the graph to look like a straight line, rising diagonally. It’s not. (As it is, this model predicted that we would only get 11,780 students. We crossed that line about 2 weeks ago.
So we know that our model must take into account the faster growth, but those leaps in the data are changes that caused by things outside of our control – EdX sending out a mail message appears to cause a jump that’s roughly 800-1,600 students, and it persists for a couple of days.
Let’s look at what the models predicted. Assumption 2 predicted a final student number around 15,680. Uhh. No. Assumption 3 predicted a final student number around 17,000, with an upper bound of 17,730.
Hmm. Interesting. We’ve just hit 17,571 so it looks like all of our measures need to take into account the “EdX” boost. But, as estimates go, Assumption 3 gave us a workable ballpark and we’ll probably use it again for the next time that we do this.
Now let’s look at demographic data. We now we have 171-172 countries (it varies a little) but how are we going for participation across gender, age and degree status? Giving this information to EdX is totally voluntary but, as long as we take that into account, we make some interesting discoveries.
Our median student age is 25, with roughly 40% under 25 and roughly 40% from 26 to 40. That means roughly 20% are 41 or over. (It’s not surprising that the graph sits to one side like that. If the left tail was the same size as the right tail, we’d be dealing with people who were -50.)
The gender data is a bit harder to display because we have four categories: male, female, other and not saying. In terms of female representation, we have 34% of students who have defined their gender as female. If we look at the declared male numbers, we see that 58% of students have declared themselves to be male. Taking into account all categories, this means that our female participant percentage could be as high as 40% but is at least 34%. That’s much higher than usual participation rates in face-to-face Computer Science and is really good news in terms of getting programming knowledge out there.
We’re currently analysing our growth by all of these groupings to work out which approach is the best for which group. Do people prefer Twitter, mail-out, community linkage or what when it comes to getting them into the course.
Anyway, lots more to think about and many more posts to come. But we’re on and going. Come and join us!
Musing on Industrial Time
Posted: April 20, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, time banking, universal principles of design, work/life balance, workload 3 CommentsI caught up with a good friend recently and we were discussing the nature of time. She had stepped back from her job and was now spending a lot of her time with her new-born son. I have gone to working three days a week, hence have also stepped back from the five-day grind. It was interesting to talk about how this change to our routines had changed the way that we thought of and used time. She used a term that I wanted to discuss here, which was industrial time, to describe the clock-watching time of the full-time worker. This is part of the larger area of time discipline, how our society reacts to and uses time, and is really quite interesting. Both of us had stopped worrying about the flow of time in measurable hours on certain days and we just did things until we ran out of day. This is a very different activity from the usual “do X now, do Y in 15 minutes time” that often consumes us. In my case, it took me about three months of considered thought and re-training to break the time discipline habits of thirty years. In her case, she has a small child to help her to refocus her time sense on the now.
Modern time-sense is so pervasive that we often don’t think about some of the underpinnings of our society. It is easy to understand why we have years and, although they don’t line up properly, months given that these can be matched to astronomical phenomena that have an effect on our world (seasons and tides, length of day and moonlight, to list a few). Days are simple because that’s one light/dark cycle. But why there are 52 weeks in a year? Why are there 7 days in a week? Why did the 5-day week emerge as a contiguous block of 5 days? What is so special about working 9am to 5pm?
A lot of modern time descends from the struggle of radicals and unionists to protect workers from the excesses of labour, to stop people being worked to death, and the notion of the 8 hour day is an understandable division of a 24 hour day into three even chunks for work, rest and leisure. (Goodness, I sound like I’m trying to sell you chocolate!)
If we start to look, it turns out that the 7 day week is there because it’s there, based on religion and tradition. Interestingly enough, there have been experiments with other week lengths but it appears hard to shift people who are used to a certain routine and, tellingly, making people wait longer for days off appears to be detrimental to adoption.
If we look at seasons and agriculture, then there is a time to sow, to grow, to harvest and to clear, much as there is a time for livestock to breed and to be raised for purpose. If we look to the changing time of sunrise and sunset, there is a time at which natural light is available and when it is not. But, from a time discipline perspective, these time systems are not enough to be able to build a large-scale, industrial and synchronised society upon – we must replace a distributed, loose and collective notion of what time is with one that is centralised, authoritarian and singular. While religious ceremonies linked to seasonal and astronomical events did provide time-keeping on a large scale prior to the industrial revolution, the requirement for precise time, of an accuracy to hours and minutes, was not possible and, generally, not required beyond those cues given from nature such as dawn, noon, dusk and so on.
After the industrial revolution, industries and work was further developed that was heavily separated from a natural linkage – there are no seasons for a coal mine or a steam engine – and the development of the clock and reinforcement of the calendar of work allowed both the measurement of working hours (for payment) and the determination of deadlines, given that natural forces did not have to be considered to the same degree. Steam engines are completed, they have no need to ripen.
With the notion of fixed and named hours, we can very easily determine if someone is late when we have enough tools for measuring the flow of time. But this is, very much, the notion of the time that we use in order to determine when a task must be completed, rather than taking an approach that accepts that the task will be completed at some point within a more general span of time.
We still have confusion where our understanding of “real measures” such as days, interact with time discipline. Is midnight on the 3rd of April the second after the last moment of April the 2nd or the second before the first moment of April the 4th? Is midnight 12:00pm or 12:00am? (There are well-defined answers to this but the nature of the intersection is such that definitions have to be made.)
But let’s look at teaching for a moment. One of the great criticisms of educational assessment is that we confuse timeliness, and in this case we specifically mean an adherence to meeting time discipline deadlines, with achievement. Completing the work a crucial hour after it is due can lead to that work potentially not being marked at all, or being rejected. But we do usually have over-riding reasons for doing this but, sadly, these reasons are as artificial as the deadlines we impose. Why is an Engineering Degree a four-year degree? If we changed it to six would we get better engineers? If we switched to competency based training, modular learning and life-long learning, would we get more people who were qualified or experienced with engineering? Would we get less? What would happen if we switched to a 3/1/2/1 working week? Would things be better or worse? It’s hard to evaluate because the week, and the contiguous working week, are so much a part of our world that I imagine that today is the first day that some of you have thought about it.
Back to education and, right now, we count time for our students because we have to work out bills and close off accounts at end of financial year, which means we have to meet marking and award deadlines, then we have to project our budget, which is yearly, and fit that into accredited degree structures, which have year guidelines…
But I cannot give you a sound, scientific justification for any of what I just wrote. We do all of that because we are caught up in industrial time first and we convince ourselves that building things into that makes sense. Students do have ebb and flow. Students are happier on certain days than others. Transition issues on entry to University are another indicator that students develop and mature at different rates – why are we still applying industrial time from top to bottom when everything we see here says that it’s going to cause issues?
Oh, yes, the “real world” uses it. Except that regular studies of industrial practice show that 40 hour weeks, regular days off, working from home and so on are more productive than the burn-out, everything-late, rush that we consider to be the signs of drive. (If Henry Ford thinks that making people work more than 40 hours a week is bad for business, he’s worth listening to.) And that’s before we factor in the development of machines that will replace vast numbers of human jobs in the next 20 years.
I have a different approach. Why aren’t we looking at students more like we regard our grape vines? We plan, we nurture, we develop, we test, we slowly build them to the point where they can produce great things and then we sustain them for a fruitful and long life. When you plant grape vines, you expect a first reasonable crop level in three years, and commercial levels at five. Tellingly, the investment pattern for grapes is that it takes you 10 years to break even and then you start making money back. I can’t tell you how some of my students will turn out until 15-25 years down the track and it’s insanity to think you can base retrospective funding on that timeframe.
You can’t make your grapes better by telling them to be fruitful in two years. Some vines take longer than others. You can’t even tell them when to fruit (although can trick them a little). Yet, somehow, we’ve managed to work around this to produce a local wine industry worth around $5 billion dollars. We can work with variation and seasonal issues.
One of the reasons I’m so keen on MOOCs is that these can fit in with the routines of people who can’t dedicate themselves to full-time study at the moment. By placing well-presented, pedagogically-sound materials on-line, we break through the tyranny of the 9-5, 5 day work week and let people study when they are ready to, where they are ready to, for as long as they’re ready to. Like to watch lectures at 1am, hanging upside down? Go for it – as long as you’re learning and not just running the video in the background while you do crunches, of course!
Once you start to question why we have so many days in a week, you quickly start to wonder why we get so caught up on something so artificial. The simple answer is that, much like money, we have it because we have it. Perhaps it’s time to look at our educational system to see if we can do something that would be better suited to developing really good knowledge in our students, instead of making them adept at sliding work under our noses a second before it’s due. We are developing systems and technologies that can allow us to step outside of these structures and this is, I believe, going to be better for everyone in the process.
Conformity isn’t knowledge, and conformity to time just because we’ve always done that is something we should really stop and have a look at.
I want you to be sad. I want you to be angry. I want you to understand.
Posted: March 31, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, Bihar, blogging, cheating, community, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, feedback, higher education, Nick Falkner, plagiarism, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking Leave a commentNick Falkner is an Australian academic with a pretty interesting career path. He is also a culture sponge and, given that he’s (very happily) never going to be famous enough for a magazine style interview, he interviews himself on one of the more confronting images to come across the wires recently. For clarity, he’s the Interviewer (I) when he’s asking the questions.
Interviewer: As you said, “I want you to be sad. I want you to be angry. I want you to understand.” I’ve looked at the picture and I can see a lot of people who are being associated with a mass cheating scandal in the Indian state of Bihar. This appears to be a systematic problem, especially as even more cheating has been exposed in the testing for the police force! I think most people would agree that it’s a certainly a sad state of affairs and there are a lot of people I’ve heard speaking who are angry about this level of cheating – does this mean I understand? Basically, cheating is wrong?
Nick: No. What’s saddening me is that most of the reaction I’ve seen to this picture is lacking context, lacking compassion and, worse, perpetrating some of the worst victim blaming I’ve ever seen. I’m angry because people still don’t get that the system in place is Bihar, and wherever else we put systems like this, is going to lead to behaviour like this out of love and a desire for children to have opportunity, rather than some grand criminal scheme of petty advancement.
Interviewer: Well, ok, that’s a pretty strong set of statements. Does this mean that you think cheating is ok?
Nick: (laughs) Well, we’ve got the most usual response out of the way. No, I don’t support “cheating” in any educational activity because it means that the student is bypassing the learning design and, if we’ve done our job, this will be to their detriment. However, I also strongly believe that some approaches to large-scale education naturally lead to a range of behaviours where external factors can affect the perceived educational benefit to the student. In other words, I don’t want students to cheat but I know that we sometimes set things up so that cheating becomes a rational response and, in some cases, the only difference between a legitimate advantage and “cheating” is determined by privilege, access to funds and precedent.
Interviewer: Those are big claims. And you know what that means…
Nick: You want evidence! Ok. Let’s start with some context. Bihar is the third-largest state in India by population, with over 100 million people, the highest density of population in India, the largest number of people under 25 (nearly 60%), a heavily rural population (~85%) and a literacy rate around 64%. Bihar is growing very quickly but has put major work into its educational systems. From 2001 to 2011, literacy jumped from 48 to 64% – 20 of those percentage points are in increasing literacy in women alone.
If we took India out of the measurement, Bihar is in the top 11 countries in the world by population. And it’s accelerating in growth. At the same time, Bihar has lagged behind other Indian states in socio-economic development (for a range of reasons – it’s very … complicated). Historically, Bihar has been a seat of learning but recent actions, including losing an engineering college in 2000 due to boundary re-alignment, means that they are rebuilding themselves right now. At the same time, Bihar has a relatively low level of industrialisation by Indian standards although it’s redefining itself away from agriculture to services and industry at the moment, with some good economic growth. There are some really interesting projects on the horizon – the Indian Media Hub, IT centres and so on – which may bring a lot more money into the region.
Interviewer: Ok, Bihar is big, relatively poor … and?
Nick: And that’s the point. Bihar is full of people, not all of whom are literate, and many of whom still live in Indian agricultural conditions. The future is brightening for Bihar but if you want to be able to take advantage of that, then you’re going to have to be able to get into the educational system in the first place. That exam that the parents are “helping” their children with is one that is going to have an almost incomprehensibly large impact on their future…
Interviewer: Their future employment?
Nick: Not just that! This will have an impact on whether they live in a house with 24 hour power. On whether they will have an inside toilet. On whether they will be able to afford good medicine when they or their family get sick. On whether they will be able to support their parents when they get old. On how good the water they drink is. As well, yes, it will help them to get into a University system where, unfortunately, existing corruption means that money can smooth a path where actual ability has led to a rockier road. The article I’ve just linked to mentions pro-cheating rallies in Uttar Pradesh in the early 90s but we’ve seen similar arguments coming from areas where rote learning, corruption and mass learning systems are thrown together and the students become grist to a very hard stone mill. And, by similar arguments, I mean pro-cheating riots in China in 2013. Student assessment on the massive scale. Rote learning. “Perfect answers” corresponding to demonstrating knowledge. Bribery and corruption in some areas. Angry parents because they know that their children are being disadvantaged while everyone else is cheating. Same problem. Same response.
Interviewer: Well, it’s pretty sad that those countries…
Nick: I’m going to stop you there. Every time that we’ve forced students to resort to rote learning and “perfect answer” memorisation to achieve good outcomes, we’ve constructed an environment where carrying in notes, or having someone read you answers over a wireless link, suddenly becomes a way to successfully reach that outcome. The fact that this is widely used in the two countries that have close to 50% of the world’s population is a reflection of the problem of education at scale. Are you volunteering to sit down and read the 50 million free-form student essays that are produced every year in China under a fairer system? The US approach to standardised testing isn’t any more flexible. Here’s a great article on what’s wrong with the US approach because it identifies that these tests are good for measuring conformity to the test and its protocol, not the quality of any education received or the student’s actual abilities. But before we get too carried away about which countries cheat most, here are some American high school students sharing answers on Twitter.
Every time someone talks about the origin of a student, rather than the system that a student was trained under, we start to drift towards a racist mode of thinking that doesn’t help. Similar large-scale, unimaginative, conform-or-perish tests that you have to specifically study for across India, China and the US. What do we see? No real measurement of achievement or aptitude. Cheating. But let’s go back to India because the scale of the number of people involved really makes the high stakes nature of these exams even more obvious. Blow your SATs or your GREs and you can still do OK, if possibly not really well, in the US. In India… let’s have a look.
State Bank of India advertised some entry-level vacancies back in 2013. They wanted 1,500 people. 17 million applied. That’s roughly the adult population of Australia applying for some menial work at the bank. You’ve got people who are desperate to work, desperate to do something with their lives. We often think of cheats as being lazy or deceitful when it’s quite possible to construct a society so that cheating is part of a wider spectrum of behaviour that helps you achieve your goals. Performing well in exams in India and China is a matter of survival when you’re talking about those kinds of odds, not whether you get a great or an ok job.
Interviewer: You’d use a similar approach to discuss the cheating on the police exam?
Nick: Yes. It’s still something that shouldn’t be happening but the police force is a career and, rather sadly, can also be a lucrative source of alternative income in some countries. It makes sense that this is also something that people consider to be very, very high stakes. I’d put money on similar things happening in countries where achieving driving licences are a high stakes activity. (Oh, good, I just won money.)
Interviewer: So why do you want us to be sad?
Nick: I don’t actually want people to be sad, I’d much prefer it if we didn’t need to have this discussion. But, in a nutshell, every parent in that picture is actually demonstrating their love and support for their children and family. That’s what the human tragedy is here. These Biharis probably don’t have the connections or money to bypass the usual constraints so the best hope that their kids have is for their parents to risk their lives climbing walls to slip them notes.
I mean, everyone loves their kids. And, really, even those of us without children would be stupid not to realise that all children are our children in many ways, because they are the future. I know a lot of parents who saw this picture and they didn’t judge the people on the walls because they could see themselves there once they thought about it.
But it’s tragic. When the best thing you can do for your child is to help them cheat on an exam that controls their future? How sad is that?
Interviewer: Do you need us to be angry? Reading back, it sounds like you have enough anger for all of us.
Nick: I’m angry because we keep putting these systems in place despite knowing that they’re rubbish. Rousseau knew it hundreds of years ago. Dewey knew it in the 1930s. We keep pretending that exams like this sort people on merit when all of our data tells us that the best indicator of performance is the socioeconomic status of the parents, rather than which school they go to. But, of course, choosing a school is a kind of “legal” cheating anyway.
Interviewer: Ok, now there’s a controversial claim.
Nick: Not really. Studies show us that students at private schools tend to get higher University entry marks, which is the gateway to getting into courses and also means that they’ve completed their studies. Of course, the public school students who do get in go on to get higher GPAs… (This article contains the data.)
Interviewer: So it all evens out?
Nick: (laughs) No, but I have heard people say that. Basically, sending your kids to a “better” school, one of the private schools or one of the high-performing publics, especially those that offer International Baccalaureate, is not going to hurt your child’s chances of getting a good Tertiary entry mark. But, of course, the amount of money required to go to a private school is not… small… and the districting of public schools means that you have to be in the catchment to get one of these more desirable schools. And, strangely enough, once you factor in the socio-economic factors and outlook for a school district, it’s amazing how often that the high-performing schools map into higher SEF areas. Not all of them and there are some magnificent efforts in innovative and aggressive intervention in South Australia alone but even these schools have limited spaces and depend upon the primary feeder schools. Which school you go to matters. It shouldn’t. But it does.
So, you could bribe someone to make the exam easier or you could pay up to AUD $24,160 in school fees every year to put your child into a better environment. You could go to your local public school or, if you can manage the difficulty and cost of upheaval, you could relate to a new suburb to get into a “better” public school. Is that fair to the people that your child is competing against to get into limited places at University if they can’t afford that much or can’t move? That $24,000 figure is from this year’s fees for one of South Australia’s most highly respected private schools. That figure is 10 times the nominal median Indian income and roughly the same as an experienced University graduate would make in Bihar each year. In Australia, the 2013 median household income was about twice that figure, before tax. So you can probably estimate how many Australian families could afford to put one, or more, children through that kind of schooling for 5-12 years and it’s not a big number.
The Biharis in the picture don’t have a better option. They don’t have the money to bribe or the ability to move. Do you know how I know? Because they are hanging precariously from a wall trying to help their children copy out a piece of information in perfect form in order to get an arbitrary score that could add 20 years to their lifespan and save their own children from dying of cholera or being poisoned by contaminated water.
Some countries, incredibly successful education stories like Finland (seriously, just Google “Finland Educational System” and prepare to have your mind blown), take the approach that every school should be excellent, every student is valuable, every teacher is a precious resource and worthy of respect and investment and, for me, these approaches are the only way to actually produce a fair system. Excellence in education that is only available to the few makes everyone corrupt, to a greater or lesser degree, whether they realise it or not. So I’m angry because we know exactly what happens with high stakes exams like this and I want everyone to be angry because we are making ourselves do some really awful things to ourselves by constantly bending to conform to systems like this. But I want people to be angry because the parents in the picture have a choice of “doing the right thing” and watching their children suffer, or “doing the wrong thing” and getting pilloried by a large and judgemental privileged group on the Internet. You love your kids. They love their kids. We should all be angry that these people are having to scramble for crumbs at such incredibly high stakes.
But demanding that the Indian government do something is hypocritical while we use similar systems and we have the ability to let money and mobility influence the outcome for students at the expense of other students. Go and ask Finland what they do, because they’re happy to tell you how they fixed things but people don’t seem to want to actually do most of the things that they have done.
Interviewer: We’ve been talking for a while so we had better wrap up. What do you want people to understand?
Nick: What I always want people to understand – I want them to understand “why“. I want them to be able to think about and discuss why these images from a collapsing educational system is so sad. I want them to understand why our system is really no better. I want them to think about why struggling students do careless, thoughtless and, by our standards, unethical things when they see all the ways that other people are sliding by in the system or we don’t go to the trouble to construct assessment that actually rewards creative and innovative approaches.
I want people to understand that educational systems can be hard to get right but it is both possible and essential. It takes investment, it takes innovation, it takes support, it takes recognition and it takes respect. Why aren’t we doing this? Delaying investment will only make the problem harder!
Really, I want people to understand that we would have to do a very large amount of house cleaning before we could have the audacity to criticise the people in that photo and, even then, it would be an action lacking in decency and empathy.
We have never seen enough of a level playing field to make a meritocratic argument work because of ingrained privilege and disparity in opportunity.
Interviewer: So, basically, everything most people think about how education and exams work is wrong? There are examples of a fairer system but most of us never see it?
Nick: Pretty much. But I have hope. I don’t want people to stay sad or angry, I want those to ignite the next stages of action. Understanding, passion and action can change the world.
Interviewer: And that’s all we have time for. Thank you, Nick Falkner!
Why “#thedress” is the perfect perception tester.
Posted: March 2, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, Avant garde, collaboration, community, Dada, data visualisation, design, education, educational problem, ethics, feedback, higher education, in the student's head, Kazimir Malevich, learning, Marcel Duchamp, modern art, principles of design, readymades, reflection, resources, Russia, Stalin, student perspective, Suprematism, teaching, thedress, thinking 1 CommentI know, you’re all over the dress. You’ve moved on to (checks Twitter) “#HouseOfCards”, Boris Nemtsov and the new Samsung gadgets. I wanted to touch on some of the things I mentioned in yesterday’s post and why that dress picture was so useful.
The first reason is that issues of conflict caused by different perception are not new. You only have to look at the furore surrounding the introduction of Impressionism, the scandal of the colour palette of the Fauvists, the outrage over Marcel Duchamp’s readymades and Dada in general, to see that art is an area that is constantly generating debate and argument over what is, and what is not, art. One of the biggest changes has been the move away from representative art to abstract art, mainly because we are no longer capable of making the simple objective comparison of “that painting looks like the thing that it’s a painting of.” (Let’s not even start on the ongoing linguistic violence over ending sentences with prepositions.)
Once we move art into the abstract, suddenly we are asking a question beyond “does it look like something?” and move into the realm of “does it remind us of something?”, “does it make us feel something?” and “does it make us think about the original object in a different way?” You don’t have to go all the way to using body fluids and live otters in performance pieces to start running into the refrains so often heard in art galleries: “I don’t get it”, “I could have done that”, “It’s all a con”, “It doesn’t look like anything” and “I don’t like it.”
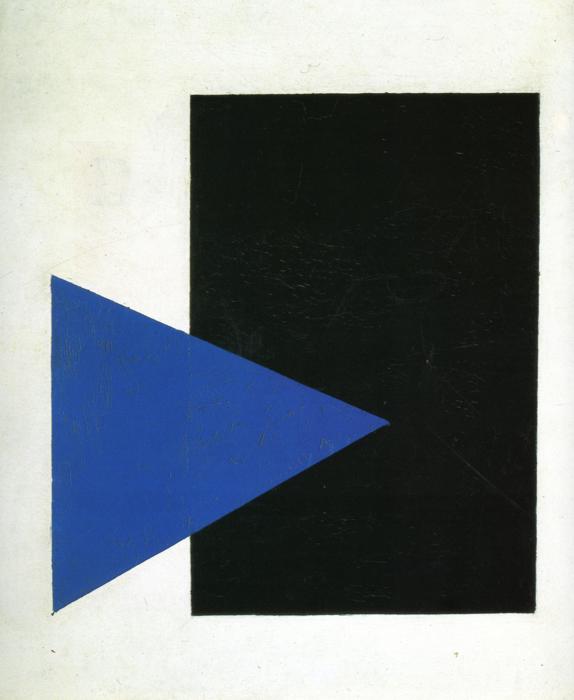
This was a radical departure from art of the time, part of the Suprematism movement that flourished briefly before Stalin suppressed it, heavily and brutally. Art like this was considered subversive, dangerous and a real threat to the morality of the citizenry. Not bad for two simple shapes, is it? And, yet, many people will look at this and use of the above phrases. There is an enormous range of perception on this very simple (yet deeply complicated) piece of art.
The viewer is, of course, completely entitled to their subjective opinion on art but this is, for many cases, a perceptual issue caused by a lack of familiarity with the intentions, practices and goals of abstract art. When we were still painting pictures of houses and rich people, there were many pictures from the 16th to 18th century which contain really badly painted animals. It’s worth going to an historical art museum just to look at all the crap animals. Looking at early European artists trying to capture Australian fauna gives you the same experience – people weren’t painting what they were seeing, they were painting a reasonable approximation of the representation and putting that into the picture. Yet this was accepted and it was accepted because it was a commonly held perception. This also explains offensive (and totally unrealistic) caricatures along racial, gender or religious lines: you accept the stereotype as a reasonable portrayal because of shared perception. (And, no, I’m not putting pictures of that up.)
But, when we talk about art or food, it’s easy to get caught up in things like cultural capital, the assets we have that aren’t money but allow us to be more socially mobile. “Knowing” about art, wine or food has real weight in certain social situations, so the background here matters. Thus, to illustrate that two people can look at the same abstract piece and have one be enraptured while the other wants their money back is not a clean perceptual distinction, free of outside influence. We can’t say “human perception is very a personal business” based on this alone because there are too many arguments to be made about prior knowledge, art appreciation, socioeconomic factors and cultural capital.
But let’s look at another argument starter, the dreaded Monty Hall Problem, where there are three doors, a good prize behind one, and you have to pick a door to try and win a prize. If the host opens a door showing you where the prize isn’t, do you switch or not? (The correctly formulated problem is designed so that switching is the right thing to do but, again, so much argument.) This is, again, a perceptual issue because of how people think about probability and how much weight they invest in their decision making process, how they feel when discussing it and so on. I’ve seen people get into serious arguments about this and this doesn’t even scratch the surface of the incredible abuse Marilyn vos Savant suffered when she had the audacity to post the correct solution to the problem.
This is another great example of what happens when the human perceptual system, environmental factors and facts get jammed together but… it’s also not clean because you can start talking about previous mathematical experience, logical thinking approaches, textual analysis and so on. It’s easy to say that “ah, this isn’t just a human perceptual thing, it’s everything else.”
This is why I love that stupid dress picture. You don’t need to have any prior knowledge of art, cultural capital, mathematical background, history of game shows or whatever. All you need are eyes and relatively functional colour sense of colour. (The dress doesn’t even hit most of the colour blindness issues, interestingly.)
The dress is the clearest example we have that two people can look at the same thing and it’s perception issues that are inbuilt and beyond their control that cause them to have a difference of opinion. We finally have a universal example of how being human is not being sure of the world that we live in and one that we can reproduce anytime we want, without having to carry out any more preparation than “have you seen this dress?”
What we do with it is, as always, the important question now. For me, it’s a reminder to think about issues of perception before I explode with rage across the Internet. Some things will still just be dumb, cruel or evil – the dress won’t heal the world but it does give us a new filter to apply. But it’s simple and clean, and that’s why I think the dress is one of the best things to happen recently to help to bring us together in our discussions so that we can sort out important things and get them done.
That’s not the smell of success, your brain is on fire.
Posted: February 11, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: authenticity, collaboration, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, Henry Ford, higher education, in the student's head, industrial research, learning, measurement, multi-tasking, reflection, resources, student perspective, students, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, time banking, work/life balance, working memory, workload Leave a commentI’ve written before about the issues of prolonged human workload leading to ethical problems and the fact that working more than 40 hours a week on a regular basis is downright unproductive because you get less efficient and error-prone. This is not some 1968 French student revolutionary musing on what benefits the soul of a true human, this is industrial research by Henry Ford and the U.S. Army, neither of whom cold be classified as Foucault-worshipping Situationist yurt-dwelling flower children, that shows that there are limits to how long you can work in a sustained weekly pattern and get useful things done, while maintaining your awareness of the world around you.
The myth won’t die, sadly, because physical presence and hours attending work are very easy to measure, while productive outputs and their origins in a useful process on a personal or group basis are much harder to measure. A cynic might note that the people who are around when there is credit to take may end up being the people who (reluctantly, of course) take the credit. But we know that it’s rubbish. And the people who’ve confirmed this are both philosophers and the commercial sector. One day, perhaps.
But anyone who has studied cognitive load issues, the way that the human thinking processes perform as they work and are stressed, will be aware that we have a finite amount of working memory. We can really only track so many things at one time and when we exceed that, we get issues like the helmet fire that I refer to in the first linked piece, where you can’t perform any task efficiently and you lose track of where you are.
So what about multi-tasking?
Ready for this?
We don’t.
There’s a ton of research on this but I’m going to link you to a recent article by Daniel Levitin in the Guardian Q&A. The article covers the fact that what we are really doing is switching quickly from one task to another, dumping one set of information from working memory and loading in another, which of course means that working on two things at once is less efficient than doing two things one after the other.
But it’s more poisonous than that. The sensation of multi-tasking is actually quite rewarding as we get a regular burst of the “oooh, shiny” rewards our brain gives us for finding something new and we enter a heightened state of task readiness (fight or flight) that also can make us feel, for want of a better word, more alive. But we’re burning up the brain’s fuel at a fearsome rate to be less efficient so we’re going to tire more quickly.
Get the idea? Multi-tasking is horribly inefficient task switching that feels good but makes us tired faster and does things less well. But when we achieve tiny tasks in this death spiral of activity, like replying to an e-mail, we get a burst of reward hormones. So if your multi-tasking includes something like checking e-mails when they come in, you’re going to get more and more distracted by that, to the detriment of every other task. But you’re going to keep doing them because multi-tasking.
I regularly get told, by parents, that their children are able to multi-task really well. They can do X, watch TV, do Y and it’s amazing. Well, your children are my students and everything I’ve seen confirms what the research tells me – no, they can’t but they can give a convincing impression when asked. When you dig into what gets produced, it’s a different story. If someone sits down and does the work as a single task, it will take them a shorter time and they will do a better job than if they juggle five things. The five things will take more than five times as long (up to 10, which really blows out time estimation) and will not be done as well, nor will the students learn about the work in the right way. (You can actually sabotage long term storage by multi-tasking in the wrong way.) The most successful study groups around the Uni are small, focused groups that stay on one task until it’s done and then move on. The ones with music and no focus will be sitting there for hours after the others are gone. Fun? Yes. Efficient? No. And most of my students need to be at least reasonably efficient to get everything done. Have some fun but try to get all the work done too – it’s educational, I hear. 🙂
It’s really not a surprise that we haven’t changed humanity in one or two generations. Our brains are just not built in a way that can (yet) provide assistance with the quite large amount of work required to perform multi-tasking.
We can handle multiple tasks, no doubt at all, but we’ve just got to make sure, for our own well-being and overall ability to complete the task, that we don’t fall into the attractive, but deceptive, trap that we are some sort of parallel supercomputer.
We don’t need no… oh, wait. Yes, we do. (@pwc_AU)
Posted: February 11, 2015 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, Australia, community, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, G20, higher education, learning, measurement, pricewaterhousecoopers, pwc, reflection, resources, science and technology, thinking, tools Leave a commentThe most important thing about having a good idea is not the idea itself, it’s doing something with it. In the case of sharing knowledge, you have to get good at communication or the best ideas in the world are going to be ignored. (Before anyone says anything, please go and review the advertising industry which was worth an estimated 14 billion pounds in 2013 in the UK alone. The way that you communicate ideas matters and has value.)
Knowledge doesn’t leap unaided into most people’s heads. That’s why we have teachers and educational institutions. There are auto-didacts in the world and most people can pull themselves up by their bootstraps to some extent but you still have to learn how to read and the more expertise you can develop under guidance, the faster you’ll be able to develop your expertise later on (because of how your brain works in terms of handling cognitive load in the presence of developed knowledge.)
When I talk about the value of making a commitment to education, I often take it down to two things: ongoing investment and excellent infrastructure. You can’t make bricks without clay and clay doesn’t turn into bricks by itself. But I’m in the education machine – I’m a member of the faculty of a pretty traditional University. I would say that, wouldn’t I?
That’s why it’s so good to see reports coming out of industry sources to confirm that, yes, education is important because it’s one of the many ways to drive an economy and maintain a country’s international standing. Many people don’t really care if University staff are having to play the banjo on darkened street corners to make ends meet (unless the banjo is too loud or out of tune) but they do care about things like collapsing investments and being kicked out of the G20 to be replaced by nations that, until recently, we’ve been able to list as developing.
PricewaterhouseCoopers (pWc) have recently published a report where they warn that over-dependence on mining and lack of investment in science and technology are going to put Australia in a position where they will no longer be one of the world’s 20 largest economies but will be relegated, replaced by Vietnam and Nigeria. If fact, the outlook is bleaker than that, moving Australia back beyond Bangladesh and Iran, countries that are currently receiving international support. This is no slur on the countries that are developing rapidly, improving conditions for their citizens and heading up. But it is an interesting reflection on what happens to a developed country when it stops trying to do anything new and gets left behind. Of course, science and technology (STEM) does not leap fully formed from the ground so this, in terms, means that we’re going to have make sure that our educational system is sufficiently strong, well-developed and funded to be able to produce the graduates who can then develop the science and technology.
We in the educational community and surrounds have been saying this for years. You can’t have an innovative science and technology culture without strong educational support and you can’t have a culture of innovation without investment and infrastructure. But, as I said in a recent tweet, you don’t have to listen to me bang on about “social contracts”, “general benefit”, “universal equity” and “human rights” to think that investing in education is a good idea. PwC is a multi-national company that’s the second largest professional services company in the world, with annual revenues around $34 billion. And that’s in hard American dollars, which are valuable again compared to the OzD. PwC are serious money people and they think that Australia is running a high risk if we don’t start looking at serious alternatives to mining and get our science and technology engines well-lubricated and running. And running quickly.
The first thing we have to do is to stop cutting investment in education. It takes years to train a good educator and it takes even longer to train a good researcher at University on top of that. When we cut funding to Universities, we slow our hiring, which stops refreshment, and we tend to offer redundancies to expensive people, like professors. Academic staff are not interchangeable cogs. After 12 years of school, they undertake somewhere along the lines of 8-10 years of study to become academics and then they really get useful about 10 years after that through practice and the accumulation of experience. A Professor is probably 30 years of post-school investment, especially if they have industry experience. A good teacher is 15+. And yet these expensive staff are often targeted by redundancies because we’re torn between the need to have enough warm bodies to put in front of students. So, not only do we need to stop cutting, we need to start spending and then commit to that spending for long enough to make a difference – say 25 years.
The next thing, really at the same time, we need to do is to foster a strong innovation culture in Australia by providing incentives and sound bases for research and development. This is (despite what happened last night in Parliament) not the time to be cutting back, especially when we are subsidising exactly those industries that are not going to keep us economically strong in the future.
But we have to value education. We have to value teachers. We have to make it easier for people to make a living while having a life and teaching. We have to make education a priority and accept the fact that every dollar spent in education is returned to us in so many different ways, but it’s just not easy to write it down on a balance sheet. PwC have made it clear: science and technology are our future. This means that good, solid educational systems from the start of primary to tertiary and beyond are now one of the highest priorities we can have or our country is going to sink backwards. The sheep’s back we’ve been standing on for so long will crush us when it rolls over and dies in a mining pit.
I have many great ethical and social arguments for why we need to have the best education system we can have and how investment is to the benefit of every Australia. PwC have just provided a good financial argument for those among us who don’t always see past a 12 month profit and loss sheet.
Always remember, the buggy whip manufacturers are the last person to tell you not to invest in buggy whips.
101 Big And Small Ways To Make A Difference In Academia
Posted: January 5, 2015 Filed under: Education | Tags: activism, advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, education, educational problem, ethics, higher education, resources, students, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, universal principles of design, workload Leave a commentThis is a quite remarkable list of ideas that I found only today. Please invest some time to read through it as you can probably find something that speaks to you about making a difference in Academia.
101 Big And Small Ways To Make A Difference In Academia.
5 Things: Stuff I’ve Learned But Recently Had (Re)Confirmed
Posted: December 1, 2014 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, data visualisation, design, education, ethics, James Watson, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, thinking, tools 1 CommentOne of the advantages of getting older is that you realise that wisdom is merely the accumulated memory of the mistakes you made that haven’t killed you yet. Our ability to communicate these lessons as knowledge to other people determines how well we can share that wisdom around but, in many cases, it won’t ring true until someone goes through similar experiences. Here are five things that I’ve recently thought about because I have had a few decades to learn about the area and then current events have brought them to the fore. You may disagree with these but, as you will read in point 4, I encourage you to write your own rather than simply disagree with me.
- Racism and sexism are scientifically unfounded and just plain dumb. We know better.
I see that James Watson is selling his Nobel prize medal because he’d like to make some donations – oh, and buy some art. Watson was, rightly, shunned for expressing his belief that African-American people were less intelligent because they were… African-American. To even start from the incredibly shaky ground of IQ measurement is one thing but to then throw a healthy dollop of anti-African sentiment on top is pretty stupid. Read the second article to see that he’s not apologetic about his statements, he just notes that “you’re not supposed to say that”. Well, given that it’s utter rubbish, no, you should probably shouldn’t say it because it’s wrong, stupid and discriminatory. Our existing biases, cultural factors and lack of equal access to opportunity are facts that disproportionately affect African-Americans and women, to mention only two of the groups that get regularly hammered over this, but to think that this indicates some sort of characteristic of the victim is biassed privileged reasoning at its finest. Read more here. Read The Mismeasure of Man. Read recent studies that are peer-reviewed in journals by actual scientists.In short, don’t buy his medal. Give donations directly to the institutions he talks about if you feel strongly. You probably don’t want to reward an unrepentant racist and sexist man with a Hockney.
- Being aware of your privilege doesn’t make it go away.
I am a well-educated white man from a background of affluent people with tertiary qualifications. I am also married to a woman. My wife and I work full-time and have long-term employment with good salaries and benefits, living in a safe country that still has a reasonable social contract. This means that I have the most enormous invisible backpack of privilege, resilience and resources, to draw upon that means that I am rarely in any form of long-term distress at all. Nobody is scared when I walk into a room unless I pick up a karaoke microphone. I will be the last person to be discriminated against. Knowing this does not then make it ok if I then proceed to use my privilege in the world as if this is some sort of natural way of things. People are discriminated against every day. Assaulted. Raped. Tortured. Killed. Because they lack my skin colour, my gender, my perceived sexuality or my resources. They have obstacles in their path to achieving a fraction of my success that I can barely imagine. Given how much agency I have, I can’t be aware of my privilege without acting to grant as much opportunity and agency as I can to other people.As it happens, I am lucky enough to have a job where I can work to improve access to education, to develop the potential of students, to support new and exciting developments that might lead to serious and positive social change in the future. It’s not enough for me to say “Oh, yes, I have some privilege but I know about it now. Right. Moving on.” I don’t feel guilty about my innate characteristics (because it wasn’t actually my choice that I was born with XY chromosomes) but I do feel guilty if I don’t recognise that my continued use of my privilege generally comes at the expense of other people. So, in my own way and within my own limitations, I try to address this to reduce the gap between the haves and the have-nots. I don’t always succeed. I know that there are people who are much better at it. But I do try because, now that I know, I have to try to act to change things.
- Real problems take decades to fix. Start now.
I’ve managed to make some solid change along the way but, in most cases, these changes have taken 2-3 years to achieve and some of them are going to be underway for generations. One of my students asked me how I would know if we’d made a solid change to education and I answered “Well, I hope to see things in place by the time I’m 50 (four years from now) and then it will take about 25 years to see how it has all worked. When I retire, at 75, I will have a fairly good idea.”This is totally at odds with election cycles for almost every political sphere that work in 3-4 years, where 6-12 months is spent blaming the previous government, 24 months is spent doing something and the final year is spent getting elected again. Some issues are too big to be handled within the attention span of a politician. I would love to see things like public health and education become bipartisan issues with community representation as a rolling component of existing government. Keeping people healthy and educated should be statements everyone can agree on and, given how long it has taken me to achieve small change, I can’t see how we’re going to get real and meaningful improvement unless we start recognising that some things take longer than 2 years to achieve.
- Everyone’s a critic, fewer are creators. Everyone could be creating.
I love the idea of the manifesto, the public declaration of your issues and views, often with your aims. It is a way that someone (or a part of some sort) can say “these are the things that we care about and this is how we will fix the world”. There’s a lot inside traditional research that falls into this bucket: the world is broken and this is how my science will fix it! The problem is that it’s harder to make a definitive statement of your own views than it is to pick holes in someone else’s. As a logorrheic blogger, I have had my fair share of criticism over time and, while much of it is in the line of valuable discourse, I sometimes wonder if the people commenting would find it more useful to clearly define everything that they believe and then put it up for all to see.There is no doubt that this is challenging (my own educational manifesto is taking ages to come together as I agonise over semantics) but establishing what you believe to be important and putting it out there is a strong statement that makes you, as the author, a creator and it helps to find people who can assist you with your aims. By only responding to someone else’s manifesto, you are restricted to their colour palette and it may not contain the shades that you need.
Knowing what you believe is powerful, especially when you clearly identify it to yourself. Don’t wait for someone else to say something you agree with so that you can press the “Like” button or argue it out in the comments. Seize the keyboard!
- Money is stupid.
If you hadn’t picked up from point 2 how far away I am from the struggle of most of the 7 billion people on this planet, then this will bang that particular nail in. The true luxury of the privileged is to look at the monetary systems that control everyone else and consider other things because they can see what life in a non-scarcity environment is like. Everyone else is too busy working to have the time or headspace to see that we make money in order to spend money in order to make money because money. There’s roughly one accountant for every 250 people in the US and this is projected to rise by 13% to 2022 at exactly the same growth rate as the economy because you can’t have money without accounting for it, entering the paperwork, tracking it and so on. In the top 25 companies in the world, we see technology companies like Apple and Microsoft, resources companies like Exxon, PetroChina and BHP Biliton, giant consumer brands like Nestlé and Procter and Gamble … and investment companies and banks. Roughly 20% of the most valuable companies in the world exist because they handle vast quantities of money – they do not produce anything else. Capitalism is the ultimate Ponzi scheme.If you’ve read much of my stuff before then you know that a carrot-and-stick approach doesn’t help you to think. Money is both carrot and stick and, surprise, surprise, it can affect mechanical and simplistic performance but it can’t drive creativity or innovation. (It can be used to build an environment to support innovation but that’s another matter.) Weird, reality distorting things happen when money comes into play. People take jobs that they really don’t want to do because it pays better than something that they are good at or love. People do terrible things to other people to make more money and then, because they’re not happier, spend even more money and wonder what’s wrong. When we associate value and marks with things that we might otherwise love, bad things often happen as we can see (humorously) in Alexei Sayle’s Marxist demolition of Strictly Come Dancing.
Money is currently at the centre of our universe and it affects our thinking detrimentally, much as working with an Earth-centred model of the solar system doesn’t really work unless you keep making weird exceptions and complications in your models of reality. There are other models which, contrary to the fear mongering of the wealthy, does not mean that everyone has to live in squalor. In fact, if everyone were to live in squalor, we’d have to throw away a lot of existing resources because we already have about three billion people already living below $2.50 a day and we certainly have the resources to do better than that. Every second child in the world is living in poverty. Don’t forget that this means that the person who was going to cure cancer, develop starship travel, write the world’s greatest novel or develop working fusion/ultra-high efficiency solar may already have been born into poverty and may be one of the 22,000 children a day to die because of poverty.
We know this and we can see that this will require long-term, altruistic and smart thinking to fix. Money, however, appears to make us short-sighted, greedy and stupid. Ergo, money is stupid. Sadly, it’s an entrenched and currently necessary stupidity but we can, perhaps, hope for something better in the future.
Ending the Milling Mindset
Posted: November 17, 2014 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, failure rate, grand challenge, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, reflection, resources, student perspective, students, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design 7 CommentsThis is the second in a set of posts that are critical of current approaches to education. In this post, I’m going to extend the idea of rejecting an industrial revolutionary model of student production and match our new model for manufacturing, additive processes, to a new way to produce students. (I note that this is already happening in a number of places, so I’m not claiming some sort of amazing vision here, but I wanted to share the idea more widely.)
Traditional statistics is often taught with an example where you try to estimate how well a manufacturing machine is performing by measuring its outputs. You determine the mean and variation of the output and then use some solid calculations to then determine if the machine is going to produce a sufficient number of accurately produced widgets to keep your employers at WidgetCo happy. This is an important measure for things such as getting the weight right across a number of bags of rice or correctly producing bottles that hold the correct volume of wine. (Consumers get cranky if some bags are relatively empty or they have lost a glass of wine due to fill variations.)
If we are measuring this ‘fill’ variation, then we are going to expect deviation from the mean in two directions: too empty and too full. Very few customers are going to complain about too much but the size of the variation can rarely be constrained in just one direction, so we need to limit how widely that fill needle swings. Obviously, it is better to be slightly too full (on average) than too empty (on average) although if we are too generous then the producer loses money. Oh, money, how you make us think in such scrubby, little ways.
When it comes to producing items, rather than filling, we often use a machine milling approach, where a block of something is etched away through mechanical or chemical processes until we are left with what we want. Here, our tolerance for variation will be set based on the accuracy of our mill to reproduce the template.
In both the fill and the mill cases, imagine a production line that travels on a single pass through loading, activity (fill/mill) and then measurement to determine how well this unit conforms to the desired level. What happens to those items that don’t meet requirements? Well, if we catch them early enough then, if it’s cost effective, we can empty the filled items back into a central store and pass them through again – but this is wasteful in terms of cost and energy, not to mention that contents may not be able to be removed and then put back in again. In the milling case, the most likely deviance is that we’ve got the milling process wrong and taken away things in the wrong place or to the wrong extent. Realistically, while some cases of recycling the rejects can occur, a lot of rejected product is thrown away.
If we run our students as if they are on a production line along these lines then, totally unsurprisingly, we start to set up a nice little reject pile of our own. The students have a single pass through a set of assignments, often without the ability to go and retake a particular learning activity. If they fail sufficient of these tests, then they don’t meet our requirements and they are rejected from that course. Now some students will over perform against our expectations and, one small positive, they will then be recognised as students of distinction and not rejected. However, if we consider our student failure rate to reflect our production wastage, then failure rates of 20% or higher start to look a little… inefficient. These failure rates are only economically manageable (let us switch off our ethical brains for a moment) if we have enough students or they are considered sufficiently cheap that we can produce at 80% and still make money. (While some production lines would be crippled by a 10% failure rate, for something like electric drive trains for cars, there are some small and cheap items where there is a high failure rate but the costing model allows the business to stay economical.) Let us be honest – every University in the world is now concerned with their retention and progression rates, which is the official way of saying that we want students to stay in our degrees and pass our courses. Maybe the single pass industrial line model is not the best one.
Enter the additive model, via the world of 3D printing. 3D printing works by laying down the material from scratch and producing something where there is no wastage of material. Each item is produced as a single item, from the ground up. In this case, problems can still occur. The initial track of plastic/metal/material may not adhere to the plate and this means that the item doesn’t have a solid base. However, we can observe this and stop printing as soon as we realise this is occurring. Then we try again, perhaps using a slightly different approach to get the base to stick. In student terms, this is poor transition from the school environment, because nothing is sticking to the established base! Perhaps the most important idea, especially as we develop 3D printing techniques that don’t require us to deposit in sequential layers but instead allows us to create points in space, is that we can identify those areas where a student is incomplete and then build up that area.
In an additive model, we identify a deficiency in order to correct rather than to reject. The growing area of learning analytics gives us the ability to more closely monitor where a student has a deficiency of knowledge or practice. However, such identification is useless unless we then act to address it. Here, a small failure has become something that we use to make things better, rather than a small indicator of the inescapable fate of failure later on. We can still identify those students who are excelling but, now, instead of just patting them on the back, we can build them up in additional interesting ways, should they wish to engage. We can stop them getting bored by altering the challenge as, if we can target knowledge deficiency and address that, then we must be able to identify extension areas as well – using the same analytics and response techniques.
Additive manufacturing is going to change the way the world works because we no longer need to carve out what we want, we can build what we want, on demand, and stop when it’s done, rather than lamenting a big pile of wood shavings that never amounted to a table leg. A constructive educational focus rejects high failure rates as being indicative of missed opportunities to address knowledge deficiencies and focuses on a deep knowledge of the student to help the student to build themselves up. This does not make a course simpler or drop the quality, it merely reduces unnecessary (and uneconomical) wastage. There is as much room for excellence in an additive educational framework – if anything, you should get more out of your high achievers.
We stand at a very interesting point in history. It is time to revisit what we are doing and think about what we can learn from the other changes going on in the world, especially if it is going to lead to better educational results.
5 Things: Ethics, Morality and Truth
Posted: October 13, 2014 Filed under: Education | Tags: curriculum, education, ethical principles, ethics, higher education, in the student's head, learning, reflection, resources, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, virtue ethics Leave a commentSometimes the only exposure my students will have to the study of ethics is (sorry, ethical philosophers) me and my “freeze-dried, snap-frozen, instant peas” version of the study of ethical issues. (In the land of the unethical, the mono-principled man is king?)
Here are a quick five things that loosely summarise my loose summaries.
- Ethics, Morals and Truth are Different Things. Morals are a person’s standards of belief concerning acceptable behaviour (we often throw around words like good and bad here). Ethics are the set of moral principles that guide a person’s behaviour or that of a group. Truth is the set of things that are real and factual, or those things that are accepted as true. Does that clear it up? Things that are true can be part of an unethical set of beliefs put together by immoral people. Immoral people can actually behave ethically consistently while still appear unethical and immoral from your group. Ethics often require you to start juggling things to work out a best or most consistent course of action, which is a luxury that we generally don’t have with the truth.
- Being Good is Not the Same Thing as Trying to Do the Right Thing. Trying to do the right thing is the field where your actions are guided by your ethical principles. Trying to be the best person you can be (Hello, Captain America) is virtue ethics. Both being good and doing the right thing can be guided by rules or by looking at outcomes but one is concerned who you are trying to be and the other is concerned with what you are trying to do. Yes, this means you can be a total ratbag as long as you behave the right way in the face of every ethical dilemma. (My apologies to any rats with bags.)
- You Can Follow Rules Or You Can Aim For The Best Outcome (Or Do Both, Actually). There are two basic breakdowns I’ve mentioned before: one follows rules and by doing that then the outcome doesn’t matter, the other tries to get the best outcome and this excuses any rules you break on the way to your good outcome. Or you can mix them together and hybridise it, even throwing in virtue ethics, which is what we tend to do because very few of us are moral philosophers and most of us are human beings. 🙂
- Consistency is Important. If you make decisions one way when it’s you and another way when it’s someone else then there’s a very good chance that you’re not applying a consistent ethical framework, you’re rationalising. (Often referred to as special pleading because you are special and different.) If you treat one group of people one way, and another completely differently, then I think you can guess that your ethics are too heavily biassed to actually be considered consistent – or all that ethical.
- Questioning Your Existing Frameworks Can Be Very Important. The chances that you managed to get everything right as you moved into adulthood is, really, surprisingly low, especially as most ethical and moral thinking is done in response to situations in your life. However, it’s important to think about how you can change your thinking in a way that forms a sound and consistent basis to build your ethical thinking upon. This can be very, very challenging, especially when the situation you’re involved in is particular painful or terrifying.
And that’s it. A rapid, shallow run through a deeply complex and rewarding area that everyone should delve into at some stage in their lives.