The Continuum of Ethical Challenge: Why the Devil Isn’t Waiting in the Alleyway and The World is Harder than Bioshock.
Posted: June 15, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, community, curriculum, design, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, principles of design, reflection, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking Leave a commentThis must be a record for a post title but I hope to keep the post itself shortish. Years ago, when I was still at school, a life counsellor (who was also a pastor) came to talk to us about life choices and ethics. He was talking about the usual teen cocktail: sex, drugs and rebellion.. However, he made an impression on me by talking about his early idea of temptation. Because of the fire and brimstone preaching he’d grown up with, he half expected temptation to take the form of the Devil, beckoning him into an alleyway to take an illicit drag on a cigarette. As he grew up, and grew wiser, he realised that living ethically was really a constant set of choices, interlocking or somewhat dependant, rather than an easy life periodically interrupted by strictly defined challenges that could be overcome with a quick burst of willpower.
I recently started replaying the game Bioshock, which I have previously criticised elsewhere, and was struck by the facile nature of the much-vaunted ethical aspect to game play. For those who haven’t played it, you basically have a choice between slaughtering or saving little girls – apart from that, you have very little agency or ability to change the path you’re on. In fact, rather than provide you with the continual dilemma of whether you should observe, ignore or attack the inhabitants of the game world, you very quickly realise that there are no ‘good’ people in the world (or there are none that you are actually allowed to attack, they are all carefully shielded from you) so you can reduce your ‘choices’ when encountering a figure crouching over a pram to “should I bludgeon her to death, or set her on fire and shoot her in the head”. (It’s ok, if you try anything approaching engagement, she will try and kill you.) In fact, one of the few ‘innocents’ in the game is slaughtered in front of you while you watch impotently. So your ethical engagement is restricted, at very distinctly defined intervals, to either harvesting or rescuing the little girls who have been stolen from orphanages and turned into corpse scavenging monsters. This is as ridiculous as the intermittent Devil in the alleyway, in fact, probably more so!
I completely agree with that counsellor from (goodness) 30 years ago – it would be a nonsense to assume that tests of our ethics can be conveniently compartmentalised to a time when our resolve is strong and can be so easily predicted. The Bioshock model (or models like it, such as Call of Duty 4, where everyone is an enemy or can’t be shot in a way that affects our game beyond a waggled finger and being taken back to a previous save) is flawed because of the limited extent of the impact of the choices you make – in fact, Bioshock is particularly egregious because the ‘outcome’ of your moral choice has no serious game impact except to show you a different movie at the end. Before anyone says “it’s only a game”, I agree, but they were the ones who imposed the notion that this ethical choice made a difference. Games such as Deus Ex gave you very much un-cued opportunities to intervene or not – with changes to the game world depending on what happened. As a result, people playing Deus Ex had far more moral engagement with the game and everyone I’ve spoken to felt as if they were making the choices that led to the outcome: autonomy, mastery and purpose anyone? That was in 2000 – very few games actually see the world as one that you can influence (although some games are now coming up to par on this).
I think about this a lot for my learning design. While my students may recognise ethical choices in the real world, I am always concerned that a learning design that reduces their activities to high stakes hurdle challenges will mimic the situation where we have, effectively, put the Devil in the alleyway and you can switch on your ‘ethical’ brain at this point. I posed a question to my students in their sample exam where I proposed that they had commissioned someone to write their software for an assignment – and them asked to think about the effect that this decision would have on their future self in terms of knowledge development, if we assumed that they would always be better prepared if they did the work themselves. This takes away the focus from the day or so leading up to an individual assignment and starts to encourage continuum thinking, where every action is take as part of a whole life of ethical actions. I’m a great believer that skills only develop with practice and knowledge only stays in your head when you reinforce it, so any opportunity to encourage further development of ethical thinking is to be encouraged!
Time to Work and Time to Play
Posted: May 19, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, education, educational problem, educational research, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, work/life balance, workload 1 CommentI do a lot of grounded theory research into student behaviour patterns. It’s a bit Indiana Jones in a rather dry way: hear a rumour of a giant cache of data, hack your way through impenetrable obfuscation and poor data alignment to find the jewel at the centre, hack your way out and try to get it to the community before you get killed by snakes, thrown into a propellor or eaten. (Perhaps the analogy isn’t perfect but how recently have you been through a research quality exercise?) Our students are all pretty similar, from the metrics I have, and I’ve gone on at length about this in other posts: hyperbolic time-discounting and so on. Embarrassingly recently, however, I was introduced to the notion of instrumentality, the capability to see that achieving a task now will reduce the difficulty in completing a goal later. If we can’t see how important this is to getting students to do something, maybe it’s time to have a good sit-down and a think! Husman et al identify three associated but distinguishable aspects to a student’s appreciation of a task: how much they rate its value, their intrinsic level of motivation, and their appreciation of the instrumentality. From this study, we have a basis for the confusing and often paradoxical presentation of a student who is intelligent and highly motivated – but just not for the task we’ve given them, despite apparently and genuinely being aware of the value of the task. Without the ability to link this task to future goal success, the exponential approach of the deadline horizon can cause a student to artificially inflate the value of something of less final worth, because the actual important goal is out of sight. But rob a student of motivation and we have to put everything into a high-stakes, heavily temporally fixed into the almost immediate future and the present, often resorting to extrinsic motivating factors (bribes/threats) to impose value. This may be why everyone who uses a punishment/reward situation achieves compliance but then has to keep using this mechanism to continue to keep values artificially high. Have we stumbled across an Economy of Pedagogy? I hope not, because I can barely understand basic economics. But we can start to illustrate why the student has to be intrinsically connected to the task and the goal framework – without it, it’s carrot/stick time and, once we do that, it’s always carrot/stick time.
Like almost every teacher I know, all of my students are experts at something but mining that can be tricky. What quickly becomes apparent, and as McGonigall reflected on in “Reality is Broken”, is that people will put far more effort into an activity that they see as play than one which they see as work. I, for example, have taken up linocut printing and, for no good reason at all, have invested days into a painstaking activity where it can take four hours to achieve even a simple outcome of reasonable quality – and it will be years before I’m good at it. Yet the time I spend at the printing studio on Saturdays is joyful, recharging and, above all, playful. If I consumed 6 hours marking assignments, writing a single number out of 10 and restricting my comments to good/bad/try harder, then I would feel spent and I would dread starting, putting it off as long as possible. Making prints, I consumed about 6 hours of effort to scan, photoshop, trim, print, reverse, apply over carbon paper, trace, cut out of lino and then manually and press print about four pieces of paper – and I felt like a new man. No real surprises here. In both cases, I am highly motivated. One task has great value to my students and me because it provides useful feedback. The artistic task has value to me because I am exploring new forms of art and artistic thinking, which I find rewarding.
But what of the instrumentality? In the case of the marking, it has to be done at a time where students can get the feedback at a time where they can use it and, given we have a follow-up activity of the same type for more marks, they need to get that sooner rather than later. If I leave it all until the end of the semester, it makes my students’ lives harder and mine, too, because I can’t do everything at once and every single ‘when is it coming’ query consumes more time. In the case of the art, I have no deadline but I do have a goal – a triptych work to put on the wall in August. Every print I make makes this final production easier. The production of the lino master? Intricate, close work using sharp objects and it can take hours to get a good result. It should be dull and repetitive but it’s not – but ask me to cut out 10 of the same thing or very, very similar things and I think it would be, very quickly. So, even something that I really enjoy becomes mundane when we mess with the task enough or get to the point, in this case, where we start to say “Well, why can’t a machine do this?” Rephrasing this, we get the instrumentality focus back again: “What do I gain in the future from doing this ten times if I will only do this ten times once?” And this is a valid question for our students, too. Why should they write “Hello, World” – it has most definitely and definitively been written. It’s passed on. It is novel no more. Bereft of novelty, it rests on its laurels. If we didn’t force students to write it, there is no way that this particular phrase, which we ‘owe’ to Brian Kernighan, is introducing anyone to anything that could not have a modicum of creativity added to it by saying in the manual “Please type a sentence into this point in the program and it will display it back to you.” It is an ex-program.
I love lecturing. I love giving tutorials. I will happily provide feedback in pracs. Why don’t I like marking? It’s easy to say “Well, it’s dull and repetitive” but, if I wouldn’t ask a student to undertake a task like that so why am I doing it? Look, I’m not advocating that all marking is like this but, certainly, the manual marking of particular aspects of software does tend to be dull.
Unless, of course, you start enjoying it and we can do that if we have enough freedom and flexibility to explore playful aspects. When I marked a big group of student assignments recently, I tried to write something new for each student and, this doesn’t always succeed for small artefacts with limited variability, I did manage to complement a student on their spanish variable names, provide personalised feedback to some students who had excelled and, generally, turned a 10 mark program into a place where I thought about each student personally and then (more often than not) said something unique. Yes, sometimes the same errors cropped up and the copy/paste is handy – but by engaging with the task and thinking about how much my future interactions with the students would be helped with a little investment now, the task was still a slog, but I came out of it quite pleased with the overall achievement. The task became more enjoyable because I had more flexibility but I also was required to be there to be part of the process, I was necessary. It became possible to be (professionally and carefully) playful – which is often how I approach teaching.
Any of you who are required to use standardised tests with manual marking: you already know how desperately dull the grading is and it is a grindingly dull, rubric-bound, tick/flick scenario that does nothing except consume work. It’s valuable because it’s required and money is money. Motivating? No. Any instrumentality? No, unless giving the test raises the students to the point where you get improved circumstances (personal/school) or you reduce the amount of testing required for some reason. It is, sadly, as dull for your students to undertake them, in this scenario, because they will know how it’s marked and it is not going to trigger any of Husman’s three distinguished but associated variables.
I am never saying that everything has to fun or easy, because I doubt many areas would be able to convey enough knowledge under these strictures, but providing tasks that have room to encourage motivation, develop a personal sense of task value, and that allow students to play, potentially bringing in some of their own natural enthusiasm on other areas or channeling it here, solves two thirds of the problem in getting students involved. Intentionally grounding learning in play and carefully designing materials to make this work can make things better. It also makes it easier for staff. Right now, as we handle the assignment work of the course I’m currently teaching, other discussions on the student forums includes the History of Computing, Hofstede’s Cultural Dimensions, the significance of certain questions in the practical, complexity theory and we have only just stopped the spontaneous student comparison of performance at a simple genetic algorithms practical. My students are exploring, they are playing in the space of the discipline and, by doing so, are moving more deeply into a knowledge of taxonomy and lexicon within this space. I am moving from Lion Tamer to Ringmaster, which is the logical step to take as what I want is citizens who are participating because they can see value, have some level of motivation and are forming their instrumentality. If learning and exploration is fun now, then going further in this may lead to fun later – the future fun goal is enhanced by achieving tasks now. I’m not sure if this is necessarily the correct first demonstration of instrumentality, but it is a useful one!
However, it requires time for both the staff member to be able to construct and moderate such an environment, especially if you’re encouraging playful exploration of areas on public discussion forums, and the student must have enough time to be able to think about things, make plans and then to try again if they don’t pick it all up on the first go. Under strict and tight deadlines, we know the creativity can be impaired when we enforce the deadlines the wrong way, and we reduce the possibility of time for exploration and play – for students and staff.
Playing is serious business and our lives are better when we do more of it – the first enabling act of good play is scheduling that first play date and seeing how it goes. I’ve certainly found it to be helpful, to me and to my students.
The Kids are Alright (within statistical error)
Posted: April 21, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: blogging, community, data visualisation, design, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, reflection, thinking, tools 3 CommentsYou may have seen this quote, often (apparently inaccurately) attributed to Socrates:
“The children now love luxury; they have bad manners, contempt for authority; they show disrespect for elders and love chatter in place of exercise. Children are now tyrants, not the servants of their households. They no longer rise when elders enter the room. They contradict their parents, chatter before company, gobble up dainties at the table, cross their legs, and tyrannize their teachers.” (roughly 400BC)
Apparently this is either a paraphrase of Aristophanes or misquoted Plato – like all things attributed to Socrates, we have to remember that we don’t have his signature to any of them. However, it doesn’t really matter if Socrates said it because not only did Hesiod say something in 700BC:
“I see no hope for the future of our people if they are dependent on frivolous youth of today, for certainly all youth are reckless beyond words… When I was young, we were taught to be discreet and respectful of elders, but the present youth are exceedingly wise [disrespectful] and impatient of restraint”
And then we have Peter the Hermit in 1274AD:
“The world is passing through troublous times. The young people of today think of nothing but themselves. They have no reverence for parents or old age. They are impatient of all restraint. They talk as if they knew everything, and what passes for wisdom with us is foolishness with them. As for the girls, they are forward, immodest and unladylike in speech, behavior and dress.”
(References via the Wikiquote page of Socrates and a linked discussion page.)
Let me summarise all of this for you:
You dang kids! Get off my lawn.
As you know, I’m a facty-analysis kind of guy so I thought that, if these wise people were correct and every generation is steadily heading towards mental incapacity and moral turpitude, we should be able to model this. (As an aside, I love the word turpitude, it sounds like the state of mind a turtle reaches after drinking mineral spirits.)
So let’s do this, let’s assume that all of these people are right and that the youth are reckless, disrespectful and that this keeps happening. How do we model this?
It’s pretty obvious that the speakers in question are happy to set themselves up as people who are right, so let’s assume that a human being’s moral worth starts at 100% and that all of these people are lucky enough to hold this state. Now, since Hesiod is chronologically the first speaker, let’s assume that he is lucky enough to be actually at 100%. Now, if the kids aren’t alright, then every child born will move us away from this state. If some kids are ok, then they won’t change things. Of course, every so often we must get a good one (or Socrates’ mouthpiece and Peter the Hermit must be aliens) so there should be a case for positive improvement. But we can’t have a human who is better than 100%, work with me here, and we shall assume that at 0% we have the worst person you can think of.
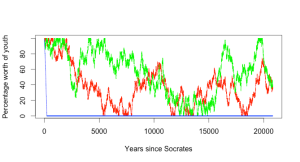
What we are now modelling is a random walk, starting at 100 and then adding some combination of -1, 0 or 1 at some regular interval. Let me cut to the chase and show you what this looks like, when modelled. I’ve assumed, for ease of modelling, that we make the assessment of the children every year and we have at most a 1 percentile point shift in that year, whatever other assumptions I made. I’ve provided three different models, one where the kids are terrible – we choose very year from no change or a negative shift. The next model is that the kids have some hope but sometimes do nothing, and we choose from an improvement, no change or steady moral decline! The final model is one where we either go up or down. Let’s look at a random walk across all three models over the span of years from 700BC to today:
As you can see, if we take the dire predictions of the next generation as true, then it is only a few hundred years before everything collapses. However, as expected, random walks over this range move around and hit a range of values. (Right now, you should look up Gambler’s Ruin to see why random walks are interesting – basically, over an infinite time, you’d expect to hit all of the values in the range from 0 to 100 an infinite number of times. This is why gamblers with small pots of money struggle against casinos with effectively infinite resources. Maths.)
But we know that the ‘everything is terrible’ model doesn’t work because both Socrates and Peter the Hermit consider themselves to be moral and both lived after the likely ‘decline to zero’ point shown in the blue line. But what would happen over longer timeframes? Let’s look at 20,000 and 200,000 years respectively. (These are separately executed random walks so the patterns will be different in each graph.)
What should be apparent, even with this rather pedantic exploration of what was never supposed to be modelled is that, even if we give credence to these particular commentators and we accept that there is some actual change that is measurable and shows an improvement or decline between generations, the negative model doesn’t work. The longer we run this, the more it will look like the noise that it is – and that is assuming that these people were right in the first place.
Personally, I think that the kids of this generation are pretty much the same as the one before, with some different adaptation to technology and societal mores. Would I have wasted time in lectures Facebooking if I had the chance? Well, I wasted it doing everything else so, yes, probably. (Look around your next staff meeting to see how many people are checking their mail. This is a technological shift driven by capability, not a sign of accelerating attention deficit.) Would I have spent tons of times playing games? Would I? I did! They were just board, role-playing and simpler computer games. The kids are alright and you can see that from the graphs – within statistical error.
Every time someone tells me that things are different, but it’s because the students are not of the same calibre as the ones before… well, I look at these quotes over the past 2,500 and I wonder.
And I try to stay off their lawn.
SIGCSE 2013: Special Session on Designing and Supporting Collaborative Learning Activities
Posted: March 31, 2013 Filed under: Education | Tags: authenticity, community, curriculum, education, educational problem, educational research, feedback, higher education, in the student's head, learning, principles of design, reflection, resources, sigcse, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design Leave a commentKatrina and I delivered a special session on collaborative learning activities, focused on undergraduates because that’s our area of expertise. You can read the outline document here. We worked together on the underlying classroom activities and have both implemented these techniques but, in this session, Katrina did most of the presenting and I presented the collaborative assessment task examples, with some facilitation.
The trick here is, of course, to find examples that are both effective as teaching tools and are effective as examples. The approach I chose to take was to remind everyone in the room of what the most important aspects were to making this work with students and I did this by deliberately starting with a bad example. This can be a difficult road to walk because, when presenting a bad example, you need to convince everyone that your choice was deliberate and that you actually didn’t just stuff things up.
My approach was fairly simple. Break people into groups, based on where they were currently sitting, and then I immediately went into the question, which had been tailored for the crowd and for my purposes:
“I want you to talk about the 10 things that you’re going to do in the next 5 years to make progress in your career and improve your job performance.”
And why not? Everyone in the room was interested in education and, most likely, had a job at a time when it’s highly competitive and hard to find or retain work – so everyone has probably thought about this. It’s a fair question for this crowd.
Well, it would be, if it wasn’t so anxiety inducing. Katrina and I both observed a sea of frozen faces as we asked a question that put a large number of participants on the spot. And the reason I did this was to remind everyone that anxiety impairs genuine participation and willingness to engage. There were a large number of frozen grins with darting eyes, some nervous mumbles and a whole lot of purposeless noise, with the few people who were actually primed to answer that question starting to lead off.
I then stopped the discussion immediately. “What was wrong with that?” I asked the group.
Well, where do we start? Firstly, it’s an individual activity, not a collaborative activity – there’s no incentive or requirement for discussion, groupwork or anything like that. Secondly, while we might expect people to be able to answer this, it is a highly charged and personal areas, and you may not feel comfortable discussing your five year plan with people that you don’t know. Thirdly, some people know that they should be able to answer this (or at least some supervisors will expect that they can) but they have no real answer and their anxiety will not only limit their participation but it will probably stop them from listening at all while they sweat their turn. Finally, there is no point to this activity – why are we doing this? What are we producing? What is the end point?
My approach to collaborative activity is pretty simple and you can read any amount of Perry, Dickinson, Hamer et al (and now us as well) to look at relevant areas and Contributing Student Pedagogy, where students have a reason to collaborate and we manage their developmental maturity and their roles in the activity to get them really engaged. Everyone can have difficulties with authority and recognising whether someone is making enough contribution to a discussion to be worth their time – this is not limited to students. People, therefore, have to believe that the group they are in is of some benefit to them.
So we stepped back. I asked everyone to introduce themselves, where they came from and give a fact about their current home that people might not know. Simple task, everyone can do it and the purpose was to tell your group something interesting about your home – clear purpose, as well. This activity launched immediately and was going so well that, when I tried to move it on because the sound levels were dropping (generally a good sign that we’re reaching a transition), some groups asked if they could keep going as they weren’t quite finished. (Monitoring groups spread over a large space can be tricky but, where the activity is working, people will happily let you know when they need more time.) I was able to completely stop the first activity and nobody wanted me to continue. The second one, where people felt that they could participate and wanted to say something, needed to keep going.
Having now put some faces to names, we then moved to a simple exercise of sharing an interesting teaching approach that you’d tried recently or seen at the conference and it’s important to note the different comfort levels we can accommodate with this – we are sharing knowledge but we give participants the opportunity to share something of themselves or something that interest them, without the burden of ownership. Everyone had already discovered that everyone in the group had some areas of knowledge, albeit small, that taught them something new. We had started to build a group where participants valued each other’s contribution.
I carried out some roaming facilitation where I said very little, unless it was needed. I sat down with some groups, said ‘hi’ and then just sat back while they talked. I occasionally gave some nodded or attentive feedback to people who looked like they wanted to speak and this often cued them into the discussion. Facilitation doesn’t have to be intrusive and I’m a much bigger fan of inclusiveness, where everyone gets a turn but we do it through non-verbal encouragement (where that’s possible, different techniques are required in a mixed-ability group) to stay out of the main corridor of communication and reduce confrontation. However, by setting up the requirement that everyone share and by providing a task that everyone could participate in, my need to prod was greatly reduced and the groups mostly ran themselves, with the roles shifting around as different people made different points.
We covered a lot of the underlying theory in the talk itself, to discuss why people have difficulty accepting other views, to clarify why role management is a critical part of giving people a reason to get involved and something to do in the conversation. The notion that a valid discursive role is that of the supporter, to reinforce ideas from the proposer, allows someone to develop their confidence and critically assess the idea, without the burden of having to provide a complex criticism straight away.
At the end, I asked for a show of hands. Who had met someone knew? Everyone. Who had found out something they didn’t know about other places? Everyone. Who had learned about a new teaching technique that they hadn’t known before. Everyone.
My one regret is that we didn’t do this sooner because the conversation was obviously continuing for some groups and our session was, sadly, on the last day. I don’t pretend to be the best at this but I can assure you that any capability I have in this kind of activity comes from understanding the theory, putting it into practice, trying it, trying it again, and reflecting on what did and didn’t work.
I sometimes come out of a lecture or a collaborative activity and I’m really not happy. It didn’t gel or I didn’t quite get the group going as I wanted it to – but this is where you have to be gentle on yourself because, if you’re planning to succeed and reflecting on the problems, then steady improvement is completely possible and you can get more comfortable with passing your room control over to the groups, while you move to the facilitation role. The more you do it, the more you realise that training your students in role fluidity also assists them in understanding when you have to be in control of the room. I regularly pass control back and forward and it took me a long time to really feel that I wasn’t losing my grip. It’s a practice thing.
It was a lot of fun to give the session and we spent some time crafting the ‘bad example’, but let me summarise what the good activities should really look like. They must be collaborative, inclusive, achievable and obviously beneficial. Like all good guidelines there are times and places where you would change this set of characteristics, but you have to know your group well to know what challenges they can tolerate. If your students are more mature, then you push out into open-ended tasks which are far harder to make progress in – but this would be completely inappropriate for first years. Even in later years, being able to make some progress is more likely to keep the group going than a brick wall that stops you at step 1. But, let’s face it, your students need to know that working in that group is not only not to their detriment, but it’s beneficial. And the more you do this, the better their groupwork and collaboration will get – and that’s a big overall positive for the graduates of the future.
To everyone who attended the session, thank you for the generosity and enthusiasm of your participation and I’m catching up on my business cards in the next weeks. If I promised you an e-mail, it will be coming shortly.
Expressiveness and Ambiguity: Learning to Program Can Be Unnecessarily Hard
Posted: January 23, 2013 Filed under: Education, Opinion | Tags: advocacy, collaboration, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools Leave a commentOne of the most important things to be able to do in any profession is to think as a professional. This is certainly true of Computer Science, because we have to spend so much time thinking as a Computer Scientist would think about how the machine will interpret our instructions. For those who don’t program, a brief quiz. What is the value of the next statement?
What is 3/4?
No doubt, you answered something like 0.75 or maybe 75% or possibly even “three quarters”? (And some of you would have said “but this statement has no intrinsic value” and my heartiest congratulations to you. Now go off and contemplate the Universe while the rest of us toil along on the material plane.) And, not being programmers, you would give me the same answer if I wrote:
What is 3.0/4.0?
Depending on the programming language we use, you can actually get two completely different answers to this apparently simple question. 3/4 is often interpreted by the computer to mean “What is the result if I carry out integer division, where I will only tell you how many times the denominator will go into the numerator as a whole number, for 3 and 4?” The answer will not be the expected 0.75, it will be 0, because 4 does not go into 3 – it’s too big. So, again depending on programming language, it is completely possible to ask the computer “is 3/4 equivalent to 3.0/4.0?” and get the answer ‘No’.
This is something that we have to highlight to students when we are teaching programming, because very few people use integer division when they divide one thing by another – they automatically start using decimal points. Now, in this case, the different behaviour of the ‘/’ is actually exceedingly well-defined and is not all ambiguous to the computer or to the seasoned programmer. It is, however, nowhere near as clear to the novice or casual observer.
I am currently reading Stephen Ramsay’s excellent “Reading Machines: Towards an Algorithmic Criticism” and it is taking me a very long time to read an 80 page book. Why? Because, to avoid ambiguity and to be as expressive and precise as possible, he has used a number of words and concepts with which I am unfamiliar or that I have not seen before. I am currently reading his book with a web browser and a dictionary because I do not have a background in literary criticism but, once I have the building blocks, I can understand his argument. In other words, I am having to learn a new language in order to read a book for that new language community. However, rather than being irked that “/” changes meaning depending on the company it keeps, I am happy to learn the new terms and concepts in the space that Ramsay describes, because it is adding to my ability to express key concepts, without introducing ambiguous shadings of language over things that I already know. Ramsay is not, for example, telling me that “book” no longer means “book” when you place it inside parentheses. (It is worth noting that Ramsay discusses the use of constraint as a creative enhancer, a la Oulipo, early on in the book and this is a theme for another post.)
The usual insult at this point is to trot out the accusation of jargon, which is as often a statement that “I can’t be bothered learning this” than it is a genuine complaint about impenetrable prose. In this case, the offender in my opinion is the person who decided to provide an invisible overloading of the “/” operator to mean both “division” and “integer division”, as they have required us to be aware of a change in meaning that is not accompanied by a change in syntax. While this isn’t usually a problem, spoken and written languages are full of these things after all, in the computing world it forces the programmer to remember that “/” doesn’t always mean “/” and then to get it the right way around. (A number of languages solve this problem by providing a distinct operator – this, however, then adds to linguistic complexity and rather than learning two meanings, you have to learn two ‘words’. Ah, no free lunch.) We have no tone or colour in mainstream programming languages, for a whole range of good computer grammar reasons, but the absence of the rising tone or rising eyebrow is sorely felt when we encounter something that means two different things. The net result is that we tend to use the same constructs to do the same thing because we have severe limitations upon our expressivity. That’s why there are boilerplate programmers, who can stitch together a solution from things they have already seen, and people who have learned how to be as expressive as possible, despite most of these restrictions. Regrettably, expressive and innovative code can often be unreadable by other people because of the gymnastics required to reach these heights of expressiveness, which is often at odds with what the language designers assumed someone might do.
We have spent a great deal of effort making computers better at handling abstract representations, things that stand in for other (real) things. I can use a name instead of a number and the computer will keep track of it for me. It’s important to note that writing int i=0; is infinitely preferable to typing “0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000” into the correct memory location and then keeping that (rather large number) address written on a scrap of paper. Abstraction is one of the fundamental tools of modern programming, yet we greatly limit expressiveness in sometimes artificial ways to reduce ambiguity when, really, the ambiguity does seem a little artificial.
One of the nastiest potential ambiguities that shows up a lot is “what do we mean by ‘equals'”. As above, we already know that many languages would not tell you that “3/4 equals 3.0/4.0” because both mathematical operations would be executed and 0 is not the same as 0.75. However, the equivalence operator is often used to ask so many different questions: “Do these two things contain the same thing?”, “Are these two things considered to be the same according to the programmer?” and “Are these two things actually the same thing and stored in the same place in memory?”
Generally, however, to all of these questions, we return a simple “True” or “False”, which in reality reflects neither the truth nor the falsity of the situation. What we are asking, respectively, is “Are the contents of these the same?” to which the answer is “Same” or “Different”. To the second, we are asking if the programmer considers them to be the same, in which case the answer is really “Yes” or “No” because they could actually be different, yet not so different that the programmer needs to make a big deal about it. Finally, when we are asking if two references to an object actually point to the same thing, we are asking if they are in the same location or not.
There are many languages that use truth values, some of them do it far better than others, but unless we are speaking and writing in logical terms, the apparent precision of the True/False dichotomy is inherently deceptive and, once again, it is only as precise as it has been programmed to be and then interpreted, based on the knowledge of programmer and reader. (The programming language Haskell has an intrinsic ability to say that things are “Undefined” and to then continue working on the problem, which is an obvious, and welcome, exception here, yet this is not a widespread approach.) It is an inherent limitation on our ability to express what is really happening in the system when we artificially constrain ourselves in order to (apparently) reduce ambiguity. It seems to me that we have reduced programmatic ambiguity, but we have not necessarily actually addressed the real or philosophical ambiguity inherent in many of these programs.
More holiday musings on the “Python way” and why this is actually an unreasonable demand, rather than a positive feature, shortly.
Thanks for the exam – now I can’t help you.
Posted: December 31, 2012 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, grand challenge, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, time banking, tools, universal principles of design, vygotsky, workload 1 CommentI have just finished marking a pile of examinations from a course that I co-taught recently. I haven’t finalised the marks but, overall, I’m not unhappy with the majority of the results. Interestingly, and not overly surprisingly, one of the best answered sections of the exam was based on a challenging essay question I set as an assignment. The question spans many aspects of the course and requires the student to think about their answer and link the knowledge – which most did very well. As I said, not a surprise but a good reinforcement that you don’t have to drill students in what to say in the exam, but covering the requisite knowledge and practising the right skills is often helpful.
However, I don’t much like marking exams and it doesn’t come down to the time involved, the generally dull nature of the task or the repetitive strain injury from wielding a red pen in anger, it comes down to the fact that, most of the time, I am marking the student’s work at a time when I can no longer help him or her. Like most exams at my Uni, this was the terminal examination for the course, worth a substantial amount of the final marks, and was taken some weeks after teaching finished. So what this means is that any areas I identify for a given student cannot now be corrected, unless the student chooses to read my notes in the exam paper or come to see me. (Given that this campus is international, that’s trickier but not impossible thanks to the Wonders of Skypenology.) It took me a long time to work out exactly why I didn’t like marking, but when I did, the answer was obvious.
I was frustrated that I couldn’t actually do my job at one of the most important points: when lack of comprehension is clearly identified. If I ask someone a question in the classroom, on-line or wherever, and they give me an answer that’s not quite right, or right off base, then we can talk about it and I can correct the misunderstanding. My job, after all, is not actually passing or failing students – it’s about knowledge, the conveyance, construction and quality management thereof. My frustration during exam marking increases with every incomplete or incorrect answer I read, which illustrates that there is a section of the course that someone didn’t get. I get up in the morning with the clear intention of being helpful towards students and, when it really matters, all I can do is mark up bits of paper in red ink.

Quickly, Jones! Construct a valid knowledge framework! You’re in a group environment! Vygotsky, man, Vygotsky!
A student who, despite my sweeping, and seeping, liquid red ink of doom, manages to get a 50 Passing grade will not do the course again – yet this mark pretty clearly indicates that roughly half of the comprehension or participation required was not carried out to the required standard. Miraculously, it doesn’t matter which half of the course the student ‘gets’, they are still deemed to have attained the knowledge. (An interesting point to ponder, especially when you consider that my colleagues in Medicine define a Pass at a much higher level and in far more complicated ways than a numerical 50%, to my eternal peace of mind when I visit a doctor!) Yet their exam will still probably have caused me at least some gnashing of teeth because of points missed, pointless misstatement of the question text, obscure song lyrics, apologies for lack of preparation and the occasional actual fact that has peregrinated from the place where it could have attained marks to a place where it will be left out in the desert to die, bereft of the life-giving context that would save it from such an awful fate.
Should we move the exams earlier and then use this to guide the focus areas for assessment in order to determine the most improvement and develop knowledge in the areas in most need? Should we abandon exams entirely and move to a continuous-assessment competency based system, where there are skills and knowledge that must be demonstrated correctly and are practised until this is achieved? We are suffering, as so many people have observed before, from overloading the requirement to grade and classify our students into neatly discretised performance boxes onto a system that ultimately seeks to identify whether these students have achieved the knowledge levels necessary to be deemed to have achieved the course objectives. Should we separate competency and performance completely? I have sketchy ideas as to how this might work but none that survive under the blow-torches of GPA requirements and resource constraints.
Obviously, continuous assessment (practicals, reports, quizzes and so on) throughout the semester provide a very valuable way to identify problems but this requires good, and thorough, course design and an awareness that this is your intent. Are we premature in treating the exam as a closing-off line on the course? Do we work on that the same way that we do any assignment? You get feedback, a mark and then more work to follow-up? If we threw resourcing to the wind, could we have a 1-2 week intensive pre-semester program that specifically addressed those issues that students failed to grasp on their first pass? Congratulations, you got 80%, but that means that there’s 20% of the course that we need to clarify? (Those who got 100% I’ll pay to come back and tutor, because I like to keep cohorts together and I doubt I’ll need to do that very often.)
There are no easy answers here and shooting down these situations is very much in the fish/barrel plane, I realise, but it is a very deeply felt form of frustration that I am seeing the most work that any student is likely to put in but I cannot now fix the problems that I see. All I can do is mark it in red ink with an annotation that the vast majority will never see (unless they receive the grade of 44, 49, 64, 74 or 84, which are all threshold-1 markers for us).
Ah well, I hope to have more time in 2013 so maybe I can mull on this some more and come up with something that is better but still workable.
Thinking about teaching spaces: if you’re a lecturer, shouldn’t you be lecturing?
Posted: December 30, 2012 Filed under: Education | Tags: blogging, collaboration, community, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, feedback, Generation Why, higher education, in the student's head, learning, measurement, principles of design, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, tools, universal principles of design, vygotsky Leave a commentI was reading a comment on a philosophical post the other day and someone wrote this rather snarky line:
He’s is a philosopher in the same way that (celebrity historian) is a historian – he’s somehow got the job description and uses it to repeat the prejudices of his paymasters, flattering them into thinking that what they believe isn’t, somehow, ludicrous. (Grangousier, Metafilter article 123174)
Rather harsh words in many respects and it’s my alteration of the (celebrity historian)’s name, not his, as I feel that his comments are mildy unfair. However, the point is interesting, as a reflection upon the importance of job title in our society, especially when it comes to the weighted authority of your words. From January the 1st, I will be a senior lecturer at an Australian University and that is perceived differently where I am. If I am in the US, I reinterpret this title into their system, namely as a tenured Associate Professor, because that’s the equivalent of what I am – the term ‘lecturer’ doesn’t clearly translate without causing problems, not even dealing with the fact that more lecturers in Australia have PhDs, where many lecturers in the US do not. But this post isn’t about how people necessarily see our job descriptions, it’s very much about how we use them.
In many respects, the title ‘lecturer’ is rather confusing because it appears, like builder, nurse or pilot, to contain the verb of one’s practice. One of the big changes in education has been the steady acceptance of constructivism, where the learners have an active role in the construction of knowledge and we are facilitating learning, in many ways, to a greater extent than we are teaching. This does not mean that teachers shouldn’t teach, because this is far more generic than the binding of lecturers to lecturing, but it does challenge the mental image that pops up when we think about teaching.
If I asked you to visualise a classroom situation, what would you think of? What facilities are there? Where are the students? Where is the teacher? What resources are around the room, on the desks, on the walls? How big is it?
Take a minute to do just this and make some brief notes as to what was in there. Then come back here.
It’s okay, I’ll still be here!
Adelaide Computing Education Conventicle 2012: “It’s all about the people”
Posted: December 27, 2012 Filed under: Education | Tags: acec2012, advocacy, authenticity, blogging, collaboration, community, conventicle, curriculum, design, education, educational problem, educational research, ethics, feedback, Generation Why, grand challenge, higher education, in the student's head, learning, principles of design, reconciliation, reflection, resources, student perspective, teaching, teaching approaches, thinking, universal principles of design 1 Commentacec 2012 was designed to be a cross-University event (that’s the whole point of the conventicles, they bring together people from a region) and we had a paper from the University of South Australia: ‘”It’s all about the people”; building cultural competence in IT graduates’ by Andrew Duff, Kathy Darzanos and Mark Osborne. Andrew and Kathy came along to present and the paper was very well received, because it dealt with an important need and a solid solution to address that need, which was inclusive, insightful and respectful.
For those who are not Australians, it is very important to remember that the original inhabitants of Australia have not fared very well since white settlement and that the apology for what happened under many white governments, up until very recently, was only given in the past decade. There is still a distance between the communities and the overall process of bringing our communities together is referred to as reconciliation. Our University has a reconciliation statement and certain goals in terms of representation in our staff and student bodies that reflect percentages in the community, to reduce the underrepresentation of indigenous Australians and to offer them the same opportunities. There are many challenges facing Australia, and the health and social issues in our indigenous communities are often exacerbated by years of poverty and a range of other issues, but some of the communities have a highly vested interest in some large-scale technical, ICT and engineering solutions, areas where indigenous Australians are generally not students. Professor Lester Irabinna Rigney, the Dean of Aboriginal Education, identified the problem succinctly at a recent meeting: when your people live on land that is 0.7m above sea level, a 0.9m sea-level rise starts to become of concern and he would really like students from his community to be involved in building the sea walls that address this, while we look for other solutions!
Andrea, Kathy and Mark’s aim was to share out the commitment to reconciliation across the student body, making this a whole of community participation rather than a heavy burden for a few, under the guiding statement that they wanted to be doing things with the indigenous community, rather than doing things to them. There’s always a risk of premature claiming of expertise, where instead of working with a group to find out what they want, you walk in and tell them what they need. For a whole range of very good and often heartbreaking reasons, the Australian indigenous communities are exceedingly wary when people start ordering them about. This was the first thing I liked about this approach: let’s not make the same mistakes again. The authors were looking for a way to embed cultural awareness and the process of reconciliation into the curriculum as part of an IT program, sharing it so that other people could do it and making it practical.
Their key tenets were:
- It’s all about the diverse people. They developed a program to introduce students to culture, to give them more than one world view of the dominant culture and to introduce knowledge of the original Australians. It’s an important note that many Australians have no idea how to use certain terms or cultural items from indigenous culture, which of course hampers communication and interaction.
For the students, they were required to put together an IT proposal, working with the indigenous community, that they would implement in the later years of their degree. Thus, it became part of the backbone of their entire program.
- Doing with [people], not to [people]. As discussed, there are many good reasons for this. Reduce the urge to be the expert and, instead, look at existing statements of right and how to work with other peplum, such as the UN rights of indigenous people and the UniSA graduate attributes. This all comes together in the ICUP – Indigenous Content in Undergraduate Program
How do we deal with information management in another culture? I’ve discussed before the (to many) quite alien idea that knowledge can reside with one person and, until that person chooses or needs to hand on that knowledge, that is the person that you need. Now, instead of demanding knowledge and conformity to some documentary standard, you have to work with people. Talking rather than imposing, getting the client’s genuine understanding of the project and their need – how does the client feel about this?
Not only were students working with indigenous people in developing their IT projects, they were learning how to work with other peoples, not just other people, and were required to come up with technologically appropriate solutions that met the client need. Not everyone has infinite power and 4G LTE to run their systems, nor can everyone stump up the cash to buy an iPhone or download apps. Much as programming in embedded systems shakes students out of the ‘infinite memory, disk and power’ illusion, working with other communities in Australia shakes them out of the single worldview and from the, often disrespectful, way that we deal with each other. The core here is thinking about different communities and the fact that different people have different requirements. Sometimes you have to wait to speak to the right person, rather than the available person.
The online forum has four questions that students have to find a solution to, where the forum is overseen by an indigenous tutor. The four questions are:
- What does culture mean to you?
- Post a cultural artefact that describes your culture?
- I came here to study Computer Science – not Aboriginal Australians?
- What are some of the differences between Aboriginal and non-Aboriginal Australians?
The first two are amazing questions – what is your answer to question number 2? The second pair of questions are more challenging and illustrate the bold and head-on approach of this participative approach to reconciliation. Reconciliation between all of the Australian communities requires everyone to be involved and, being honest, questions 3 and 4 are going to open up some wounds, drag some silly thinking out into the open but, most importantly, allow us to talk through issues of concern and confusion.
I suspect that many people can’t really answer question 4 without referring back to mid-50s archetypal depictions of Australian Aborigines standing on one leg, looking out over cliffs, and there’s an excellent ACMI (Australian Centre for the Moving Image) exhibit in Melbourne that discusses this cultural misappropriation and stereotyping. One of the things that resonated with me is that asking these questions forces people to think about these things, rather than repeating old mind grooves and received nonsense overheard in pubs, seen on TV and heard in racist jokes.
I was delighted that this paper was able to be presented, not least because the goal of the team is to share this approach in the hope of achieving even greater strides in the reconciliation process. I hope to be able to bring some of it to my Uni over the next couple of years.
The Emperor’s New Clothes Redux: The Sokal Hoax
Posted: December 26, 2012 Filed under: Education | Tags: advocacy, authenticity, blogging, community, derrida, design, education, educational research, ethics, feedback, higher education, post-modernism, principles of design, reflection, resources, sokal, sokal hoax, teaching approaches, thinking, tools 4 CommentsMaking way in a new area of scholarship can be challenging for many reasons, no matter how welcoming the community. One of the reasons for this is that there are points in our life where we are allowed to make larger mistakes, or be ignorant, but it is rarer for adults, especially those who are already employed within a job, to be allowed the latitude to say “I have no idea”. As I discussed yesterday, the fable of the Emperor’s New Clothes explains this dilemma well, because children have more licence to be honest to the point of tactlessness where an adult is always weighing up the implications of admitting that they cannot quite see what everyone else is talking about.
Some of you will be familiar with the Sokal Hoax, where Professor Alan Sokal, from physics at NYU, submitted an article to a journal of postmodern cultural studies. The work, “Transgressing the Boundaries: Towards a Transformative Hermeneutics of Quantum Gravity”, was accepted by the journal Social Text, which was (at the time) not practising academic peer review. Sokal did not intend for this article to be taken seriously or even expect it to published, although he did produce an article that he described it (in a follow-up article) as:
“a pastiche of Left-wing cant, fawning references, grandiose quotations, and outright nonsense . . . structured around the silliest quotations … he could find about mathematics and physics”
The entire affair is worth reading and you can find the Wikipedia summary here and a good critique about some of Sokal’s less intended consequences here (transcript of a New York Review of Books article). Regrettably, what is less clear is whether Sokal actually achieved very much, in real terms, by carrying out this action. Yes, Social Text moved to an academic peer review system and that’s generally better for all concerned. For those who don’t know, peer review is the process by which submitted articles go to a number of other people in the field and they review the work to see if it is fit to publish. This reduces the load on the editors and allows for more, and more specific, areas of expertise to be involved. It is not, however, faultless as a poor combination of peers can still lead to substandard, or plain wrong, work getting through, especially if reviewers farm the work out to their grad students or review under time constraints. It is, therefore, not all that surprising that Sokal’s deliberately targeted paper, which identified how to get a paper published by these editors in this journal, succeeded, and less surprising when you hear the editors’ account that they thought the paper needed revisions (removing much of the handwaving and contradictory footnotes) and were concerned about the article but, as the journal at the time was one of opinion, they published it anyway.
Such generosity on the part of the editors does not forgive the publication of some of the deliberate misuse of terminology and physics that Sokal uses to highlight the lack of rigour in the journal and the editorial review process. However, one of the problems I have with this is that, as a Computer Scientist speaking to Educational researchers, people often take what I say as a true account of my field, especially given that they do not have the expertise in my discipline to know (or care) about things like computability or algorithmic performance. If I were to submit a scholarly paper to a journal of education, am I doing anyone any favours by deliberately misrepresenting the aspects of my field, given that I am identified by discipline and school on submission?
Yes, people should use terms correctly and there is a great deal of misuse of science for uninformed or nefarious purposes, with some of the writings coming from post-modernist inspired writers being completely wrong. However, when one is not a physicist, one depends upon the knowledge gained from other people as to what physics is. There is a part of me that thinks that Sokal wasted an opportunity to actually fix a number of misunderstandings – for example, making a clear distinction between linear in strict mathematical and physical terms and linear, in post-Derridan terms, where the meaning is (quite deliberately) less well-defined and often pejorative. Words change. Terms change. Knowledge can still exist and continue to connect terms if we make the effort to bridge, rather than to mock or deride.
The post-modernists, especially Derrida, have attracted a great deal of negative interest, often for what appear to be semi-religious objects to their approach, although I would be the first to say that Derrida’s obsession with repurposing words, redefining concepts when it suits him, and providing grammatical constructions that further, rather than reduce, ambiguity do make him a valid target for at least a raised eyebrow on many occasions. I do not have a strong opinion as to whether the Emperor, in this case, is clothed or not, but I must be honest and say that I do not believe that the outputs and constants of science are a purely cultural construction, although I do agree that the mechanism of the scientific academy is very much a cultural artefact and if anything deserves to be reduced to its components for inspection, it is an institution that almost systematically seems to avoid recognising the contribution of women and non-western people except where unavoidable. I mention Derrida here, mostly because Derrida was the first point of media attack when Sokal’s hoax was revealed. This speaks volumes for the bravery of Sokal’s attack – when the media will leap up and put a face on a stick to wave it about because “philosophy X is all mumbo-jumbo and here is the head witch doctor” you really have to wonder what a non-peer reviewed opinion piece in a journal dedicated to same is actually achieving. Derrida thought that the major problem with the piece was that it would make a later, serious, attempt to discuss such issues impossible to achieve.
Of course, although Sokal’s Hoax is a triumph of exposing the publication of works based on their source. authority and obscurity, this is most certainly not restricted to post-modernist journals of opinion. A friend of mine called me in once to read through a paper that used such unusual terminology, for him, that he was unsure as to whether it was good or bad. Fortunately, it was in my discipline and, because I know and can use the word ontology without dying, I was able to identify it as a low-level rehash of some basic work in the field. It was sound work, using the correct terminology, but it certainly wasn’t at the level of the conference it had been sent to – to my friend, however, it was as meaningless as anything that Sokal mocked from Derrida. I am well aware that some of my areas, including knowledge management and educational research, are seen by others to be exactly the same as the post-modernist repurposing of scientific terminology that Sokal attacks.
The point is not who is lying to whom, or whether there is anything behind some of the more obscure utterings of the Post-Modernists, but it is whether deliberately winding people up with a hoax would achieve more than a genuine attempt to reach out to and correct a community, using your expertise and developing a voice in the other discipline to provide a sound translation. Epistemology, theory of knowledge, is important and I’m really not sure that hoaxing and mockery really achieves all that much, especially as, like any extrinsic punishment approach, it tells you not to do something but not how not to do it.
Pressganging Story into Service: The Dickens, you say?
Posted: December 24, 2012 Filed under: Education | Tags: a christmas carol, bill murray, blogging, charles dickens, community, education, feedback, higher education, reflection, resources, scrooged, teaching approaches, thinking, tools Leave a comment“Marley was dead” and so begins Charles Dickens’ “A Christmas Carol” which has been reprinted and remade so many times it is near impossible to avoid the cultural impact of this work in English-speaking areas. For those who have avoided it, for whatever reason, it is a simple story. An unpleasant miser, Ebenezer Scrooge, believes Christmas to be nothing but humbug, a waste of time, a period for the stupid to amuse themselves, and a way for those who work insufficiently hard to deprive him (Scrooge) of his hard-won money. Scrooge’s transformation within the book is the core of the story, initiated by the visit of his (long dead) business partner, Marley, who warns him that only a bleak and unpleasant afterlife awaits him after death. Marley tells Scrooge that three ghosts will visit him and to change while he still can.
The first ghost, Christmas Past, shows Scrooge a younger version of himself, when he was innocent and those obstacles he faced that put him onto his current (unpleasant, unloving and unloved) trajectory. The second ghost, Christmas Present, shows him the London he is in now. The joy of family and reuniting with old friends. The ghost takes Scrooge to visit the house of Bob Cratchit, Scrooge’s underpaid and overworked clerk, who lives with a large family and a seriously ill child, Tiny Tim, for whom no medical treatment is forthcoming because Scrooge pays Cratchit so little. Finally, Christmas Yet To Come arrives, and takes Scrooge on a dark journey to the death of Tiny Tim still as a young boy, Scrooge’s own death and the human vultures who pick over his belongings, and his untended grave in a dark corner of a forgotten cemetery.
Scrooge, reminded of his humanity, surrounded by humans and warned of the outcomes to others and himself of his perilous course, awakens on Christmas morning a changed man. His entire demeanour is permanently changed, not just for Christmas Day, but because he now seeks to be not just a better man, but the best man.
I have several film version of this that I like: the Patrick Stewart is good and the Bill Murray comedic-version “Scrooged” is slightly more delightful because Scrooge (Cross, in this version) is redeemed well before his course is as set. (And I like a happy ending.)
Yesterday I spoke about finding stories and myths that I could use and, even stripped of any religious overtones associated with the word Christmas, there’s still a lot to think about in the framing of A Christmas Carol. Dickens had suffered deep and lasting humiliation as a child and the engines of the Industrial Revolution had, by this time, ground up many older traditions and families along the way. Dickens appeal to the charity of those who can afford it is a core part of the work, as well as drawing back to pre-Cromwellian Christmas traditions that had been stamped out under the dour washed-out grey heel of the puritans. But, back to the framing.
The story starts with the description of Scrooge as someone who is happy with their lot, but shouldn’t be. His negative interpretation of the world is as much at odds with reality as his positive perception of the many flaws of his partner, Marley. Marley’s visit forces Scrooge to listen to the one person who could start him on his journey – because no-one else would have the authenticity to speak to him.
The journey begins with advice from a mentor who wishes you to avoid making their mistakes.
The three ghosts appear to force Scrooge to identify how he has changed, how flawed his perceptions are and that his actions, or inactions, will most likely have consequences that extend beyond his lifetime.
In order to understand why (or if we need to change), we need to understand:
- How we have already changed to this point
- What our environment really looks like
- Why change might be necessary
And none of this is any surprise for anyone who has read one, two or many self-help or realisation books – except that Dickens’ story is full of emotion and a reason for changing. In all of its forms, I have found the thread of the Cratchits to be one of the most moving. Scrooge’s loss and decline one could almost (well, I can’t but some could) write off as the unfortunate actions of a man who attained what he thought he wanted: wealth, and thus a derived happiness. Scrooge is obviously not happy but there are far too many who would ponder ‘why’ when he was so rich! (For every aphorism regarding “money not buying happiness”, there are many examples apparently to the contrary and Dave Gilmore’s famous riposte “… but it will let you park your yacht right next to it.”)
TinyTim, for me, is the core of this myth because Tim is ill, through no fault of his own but because of the time, the body and the family that he was born into. It’s not Tim’s fault but that simple fact is not enough to save him from dying – he needs other people to realise that he deserves better just because of what he is (a child) rather than who he is (a child of poor parents). Scrooge is not an evil man, although he is most certainly not a good man at the start, and the death of the child is never what he intended, because it would never have occurred to him the Cratchit would have that much of a life outside of the office. Scrooge’s indifference to the world, to the city of London, to Cratchit and to his own humanity is part of the initial transformation that he undertook, to become the Scrooge that we saw. That is the essence of Scrooge – he can change because he changed before. When Scrooge changes, he finally starts down the path to happiness, which appears to hold him in this enlightened and positively changed state for the rest of his long (and happy) life.
I enjoy the story and it’s something I always revisit leading up to Christmas because it is very easy to start getting all ‘bah, humbug’ in the face of commercialism, over expectation and the sheer hype of the holiday season. However, looking at it as a story about change, I’m forced to think about who could come to me and say “Don’t be like me”. How have I changed from where I was 20, 10 or even 5 years ago? What am I ignoring around me that I could be appreciating more?
Where will this path take me?
What would you expect to see, if the mentor and the three ghosts came to see you?